
History Project On Nationalism In India For Class 10th
Acknowledgment
Embarking on this journey into the pages of Indian history and the profound saga of nationalism has been both enlightening and rewarding. In the pursuit of crafting this project on “Nationalism in India: A Journey towards Independence,” I extend my heartfelt gratitude to the countless individuals who have contributed, directly or indirectly, to this endeavor. First and foremost, I express my sincere thanks to my history teacher for their guidance, encouragement, and unwavering support throughout this exploration. Additionally, I acknowledge the pioneering figures of the nationalist movement, whose sacrifices and resilience paved the way for an independent India. The wealth of resources, both literary and digital, has been invaluable in piecing together this narrative, and I extend my appreciation to the authors, historians, and archivists whose work forms the foundation of this project. Lastly, I am grateful to my peers for engaging in insightful discussions that have broadened my understanding of this pivotal period in Indian history. This project stands as a collective effort, a tribute to the spirit of nationalism that echoes through the corridors of time.
Introduction
In the tapestry of India’s rich and diverse history, the thread of nationalism weaves a narrative of resilience, sacrifice, and the indomitable spirit of a people seeking self-determination. Nationalism in India is not merely a historical chapter; it is a powerful force that surged through the hearts of millions, igniting the flame of independence. This fervent desire for autonomy and a collective identity found its roots in the wake of British colonial rule, as India grappled with the challenges of modernity and the erosion of traditional values. The journey towards nationalism unfolds against a backdrop of socio-economic changes, intellectual awakening, and the emergence of visionary leaders who became the vanguards of a movement that would reshape the destiny of a nation. As we delve into the complexities of this profound phenomenon, we witness the evolution of an idea that transcended geographical boundaries, uniting a diverse populace under the common aspiration of freedom. This exploration seeks to unravel the layers of nationalism in India, tracing its origins, milestones, and the transformative impact it had on shaping the course of the Indian subcontinent.
Importances Of Nationalism In India
The importance of nationalism in India transcends mere historical significance; it is a vital force that has shaped the very identity and destiny of the nation. Several key aspects underscore the profound importance of nationalism in the Indian context:
- Unity in Diversity: Nationalism played a pivotal role in unifying a diverse and culturally rich subcontinent. India, with its myriad languages, religions, and traditions, found a common thread in the form of nationalism. It provided a unifying force that helped bridge regional differences and foster a sense of collective identity among the people.
- Struggle for Independence: The nationalist movement in India was the driving force behind the struggle for independence from British colonial rule. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Subhas Chandra Bose rallied the masses, inspiring them to stand united against a common oppressor. Nationalism became the catalyst for a non-violent yet powerful resistance that eventually led to the liberation of the country in 1947.
- Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Nationalism in India has been intrinsically linked to the preservation and celebration of its rich cultural heritage. The movement emphasized the importance of safeguarding indigenous traditions, languages, and customs, countering the cultural erosion brought about by colonial influences.
- Democratic Values: The spirit of nationalism instilled a commitment to democratic principles and governance. Post-independence, the framers of the Indian Constitution drew inspiration from the nationalist ideals to establish a democratic, secular, and socialist republic. Nationalism continues to be a guiding force in upholding democratic values and fostering a sense of civic responsibility among citizens.
- Global Recognition: The success of the nationalist movement garnered international attention and admiration. India’s journey from colonial subjugation to independence served as an inspiration for other nations striving for self-determination. The importance of Indian nationalism extends beyond its borders, influencing movements for independence and social justice worldwide.
- Nation-Building and Development: Nationalism has played a crucial role in the post-independence era by contributing to nation-building and development. The sense of pride and belonging instilled by nationalism has fueled collective efforts towards progress, economic development, and social welfare.
- Cohesive Social Fabric: Nationalism has contributed to the development of a cohesive social fabric by fostering a sense of belonging and shared destiny. It promotes inclusivity, encouraging individuals from diverse backgrounds to contribute to the nation’s growth and prosperity. In conclusion, the importance of nationalism in India is deeply rooted in its ability to unify, inspire, and drive transformative change. It remains a cornerstone of the nation’s identity, influencing its past, present, and undoubtedly shaping its future trajectory.
Features Of Nationalism In India
Nationalism in India is characterized by a set of distinctive features that have shaped the country’s socio-political landscape. These features encapsulate the essence of the Indian nationalist movement and its impact on the nation. Here are key features of nationalism in India:
- Cultural Pluralism: Indian nationalism embraces the diversity of its cultural, linguistic, and religious tapestry. It acknowledges and celebrates the coexistence of various communities, languages, and traditions, emphasizing unity in diversity as a defining characteristic.
- Non-Violent Resistance: Mahatma Gandhi’s philosophy of non-violence (ahimsa) became a hallmark of Indian nationalism. The use of peaceful resistance, civil disobedience, and non-cooperation against British rule set India’s nationalist movement apart and inspired similar movements globally.
- Inclusive Vision: Indian nationalism has an inclusive vision that extends beyond regional, religious, and caste boundaries. Leaders of the nationalist movement sought to create a nation where all citizens, regardless of their background, had equal rights and opportunities.
- Anti-Imperialist Stand: The core of Indian nationalism was rooted in opposition to British colonial rule. The movement aimed at liberating India from foreign domination, reclaiming sovereignty, and establishing a self-governing nation.
- Emphasis on Self-Reliance: Nationalist leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru and Mahatma Gandhi advocated for economic self-reliance. The Swadeshi Movement, for instance, encouraged the use of indigenous goods and industries to reduce dependence on foreign products.
- Democratic Values: Indian nationalism is closely aligned with democratic principles. Post-independence, the Indian Constitution reflects the commitment to democracy, secularism, and socialism, incorporating these values into the very fabric of the nation.
- Social Justice and Equality: The nationalist movement in India emphasized the need for social justice and equality. Leaders like B.R. Ambedkar played a crucial role in advocating for the rights of marginalized communities, leading to the inclusion of affirmative action in the Constitution.
- Patriotism and Civic Duty: Nationalism in India instills a sense of patriotism and civic duty among its citizens. The idea that each individual has a role to play in the development and well-being of the nation is a recurring theme in Indian nationalist thought.
- Legacy of Secularism: Indian nationalism upholds the principle of secularism, promoting the coexistence of different religions without favoring any particular faith. This commitment to religious harmony is enshrined in the Constitution and remains integral to the nation’s ethos.
- Global Influence: The impact of Indian nationalism extends beyond national borders. The success of the Indian independence movement inspired other nations in their quests for freedom and self-determination. These features collectively contribute to the unique character of nationalism in India, reflecting a dynamic and inclusive spirit that continues to shape the country’s identity and aspirations.
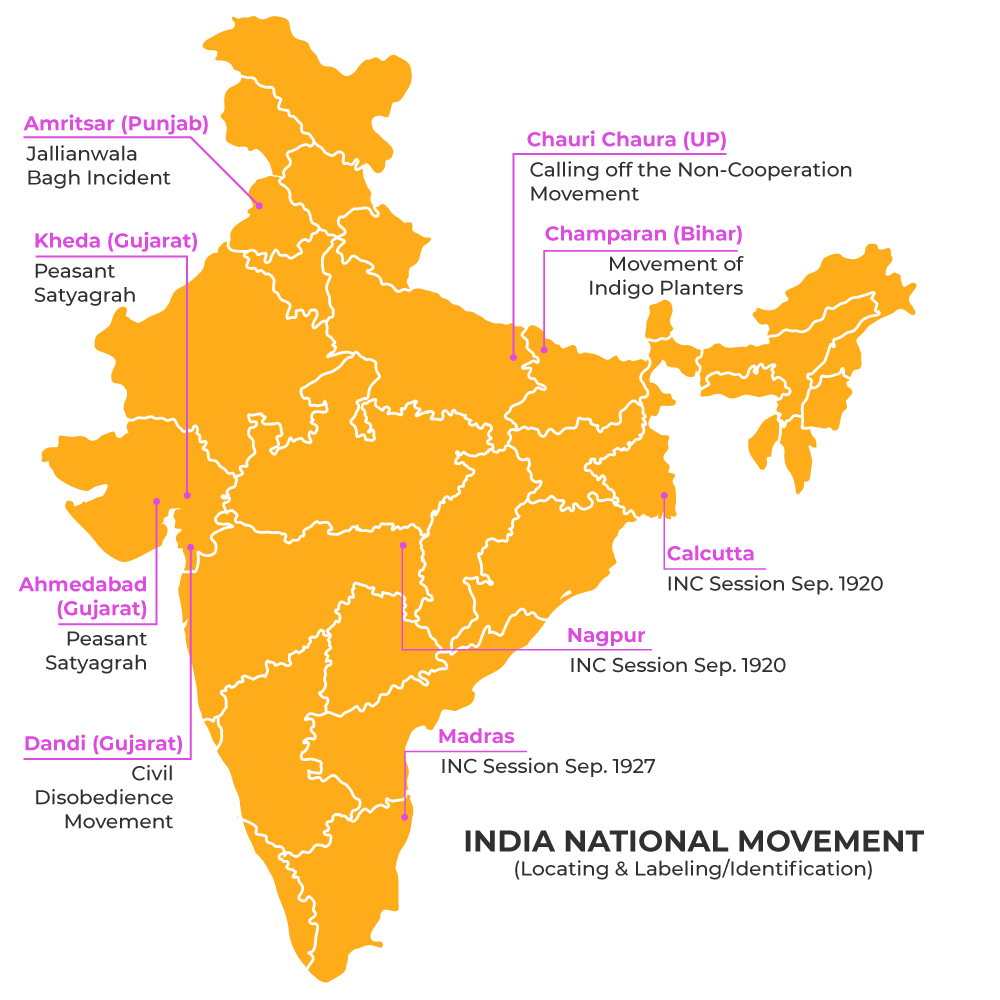
Types Of Nationalism In India
Nationalism in India has manifested in various forms, reflecting the diverse socio-cultural and political landscape of the nation. Here are several types of nationalism that have played significant roles in India:
- Cultural Nationalism: Cultural nationalism in India emphasizes the preservation and promotion of indigenous cultural practices, languages, and traditions. It seeks to celebrate the rich heritage of the country and often intertwines with movements aimed at safeguarding cultural identities.
- Religious Nationalism: This type of nationalism is rooted in religious identity, with a focus on the protection and promotion of a specific religion. In India, religious nationalism has been witnessed in movements that advocate for the interests of particular religious communities, such as Hindu nationalism or Islamic nationalism.
- Regional Nationalism: India’s diverse regions have witnessed movements advocating for greater autonomy or independence based on regional identities. Examples include movements for the creation of states like Telangana or the demand for a separate Gorkhaland in the Darjeeling region.
- Anti-Colonial Nationalism: At the core of India’s nationalist movement was the struggle against British colonial rule. Anti-colonial nationalism aimed at achieving independence and reclaiming sovereignty, uniting people across different backgrounds in a common cause.
- Secular Nationalism: Secular nationalism in India emphasizes the coexistence of various religious communities within a single political framework. It advocates for equal rights and opportunities for individuals of all religions, rejecting any form of religious discrimination.
- Socialist Nationalism: Socialist nationalism in India is associated with the vision of a socio-economic system that promotes equality and social justice. Leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru played a key role in shaping a socialist approach to nation-building, with an emphasis on equitable distribution of resources.
- Gandhian Nationalism: Inspired by Mahatma Gandhi’s philosophy of non-violence and decentralized governance, Gandhian nationalism advocates for grassroots participation, self-reliance, and moral leadership in the political sphere.
- Dalit Nationalism: Dalit nationalism focuses on the rights and empowerment of the Dalit community, historically marginalized and discriminated against. Leaders like B.R. Ambedkar played a pivotal role in advocating for Dalit rights and representation.
- Economic Nationalism: Economic nationalism in India emphasizes self-sufficiency and the development of indigenous industries. Movements such as the Swadeshi Movement aimed at reducing dependence on foreign goods and promoting economic independence.
- Feminist Nationalism: Feminist nationalism addresses issues of gender equality and women’s rights within the nationalist framework. It seeks to ensure that women have an equal role and representation in the political, social, and economic spheres of the nation. These types of nationalism coexist and often intersect in the complex socio-political landscape of India, contributing to the multifaceted nature of the country’s nationalist ethos.

Objectives Of Nationalism In India
The objectives of nationalism in India were multifaceted, reflecting the diverse challenges faced by the country under British colonial rule and the aspirations of its people. The key objectives of nationalism in India can be outlined as follows:
- Achieving Independence: The primary and overarching objective of Indian nationalism was to liberate the country from British colonial rule. The nationalist movement sought to assert India’s right to self-determination and sovereignty.
- Preserving Cultural Identity: Nationalism aimed at preserving and promoting India’s rich cultural heritage, languages, and traditions. It sought to counteract the cultural erosion caused by colonial influences and reaffirm the distinct identity of the Indian subcontinent.
- Fostering Unity among Diverse Communities: Nationalism in India aimed to unite people from diverse linguistic, religious, and cultural backgrounds. The movement emphasized the commonalities that bound the people together, fostering a sense of unity in the face of colonial oppression.
- Establishing a Democratic System: Nationalists aspired to create a democratic system of governance that would ensure representation and participation for all citizens. The idea was to replace the authoritarian colonial rule with a government that reflected the will of the people.
- Promoting Social Justice and Equality: Indian nationalism emphasized the need for social justice and equality, challenging the hierarchical social structures prevalent during colonial times. Leaders like B.R. Ambedkar advocated for the rights of marginalized communities, seeking to build a more egalitarian society.
- Economic Self-Reliance: Nationalists aimed at reducing economic dependence on the British by promoting indigenous industries and economic self-sufficiency. Movements like the Swadeshi Movement advocated for the use of locally produced goods.
- Securing Fundamental Rights: The nationalist movement sought to secure fundamental rights for all citizens, irrespective of caste, creed, or religion. The demand for civil liberties and individual freedoms was a fundamental aspect of the nationalist agenda.
- Peaceful Coexistence among Religious Communities: Nationalism in India advocated for the peaceful coexistence of various religious communities. The idea was to create a nation where individuals of different faiths could live harmoniously without religious discrimination.
- Empowering Women: Some nationalists, influenced by the ideals of social reform movements, sought to empower women and improve their status in society. The objective was to ensure equal opportunities and rights for women within the nationalist framework.
- Creating a Sovereign, United Nation: Ultimately, Indian nationalism aimed at creating a sovereign, united nation that embraced its diversity while standing firm against colonial exploitation. The vision was to establish an independent India where all citizens could contribute to the nation’s progress and well-being. These objectives collectively drove the nationalist movement in India, shaping its course and influencing the post-independence era, where efforts continued to build a democratic, inclusive, and economically vibrant nation.
Advantages Of Nationalism In India
Nationalism in India has brought about numerous advantages, shaping the nation’s identity and influencing its development. Here are key advantages of nationalism in India:
- Unity and Integration: Nationalism has played a crucial role in unifying a diverse and culturally rich nation. It has fostered a sense of common identity among people from different linguistic, religious, and cultural backgrounds, contributing to the unity and integration of India.
- Fight Against Colonialism: Nationalism was the driving force behind India’s struggle for independence from British colonial rule. The united front presented by nationalists against colonial oppression eventually led to the end of foreign domination and the establishment of a sovereign nation.
- Cultural Preservation: Nationalism has been instrumental in preserving and promoting India’s rich cultural heritage. It has encouraged the celebration of diverse traditions, languages, and artistic expressions, preventing the erosion of indigenous culture under colonial influence.
- Democratic Governance: Post-independence, nationalism played a pivotal role in shaping India’s democratic governance. The commitment to democratic principles, as reflected in the Constitution, ensures that the nation is governed by the will of the people, with equal representation and participation.
- Economic Development: Nationalism has contributed to economic development by promoting self-reliance and indigenous industries. Movements like the Swadeshi Movement aimed at reducing dependency on foreign goods, laying the foundation for economic self-sufficiency.
- International Influence: The success of the nationalist movement in India inspired similar movements around the world. India’s struggle for independence had a significant impact on global perceptions of colonialism, contributing to the decolonization process in various regions.
- Social Justice and Equality: Nationalism in India has been associated with the pursuit of social justice and equality. Efforts to eradicate caste-based discrimination and uplift marginalized communities have been integral to the nationalist agenda, fostering a more inclusive society.
- National Pride and Identity: Nationalism instills a sense of pride and identity among the citizens of India. The achievements and sacrifices of the nationalist movement continue to serve as a source of inspiration, fostering a strong national consciousness.
- Global Recognition: Independent India, born out of the nationalist struggle, gained global recognition and respect. The nation’s commitment to democratic values, secularism, and economic progress has positioned it as a prominent player on the international stage.
- Innovation and Progress: Nationalism has been a driving force behind the pursuit of innovation and progress. The collective spirit of the nation, shaped by nationalist ideals, encourages individuals to contribute to the country’s development in various fields, from science and technology to arts and literature. In summary, nationalism in India has yielded numerous advantages, ranging from the achievement of independence and cultural preservation to democratic governance and economic development. These advantages continue to shape India’s trajectory and influence its role in the global community.
Disadvantages Of Nationalism In India
While nationalism in India has brought about numerous advantages, it is essential to recognize that, like any ideology, it also has its share of disadvantages. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of nationalism in India:
- Ethnic and Religious Tensions: Nationalism, when overly focused on a specific cultural or religious identity, can exacerbate ethnic and religious tensions. In India, instances of communal violence have at times been fueled by extreme nationalist ideologies, leading to social discord.
- Regional Disparities: Excessive nationalism may sometimes neglect regional disparities, leading to an uneven distribution of resources and development. This can create tensions between different states or regions, hindering the overall progress of the nation.
- Exclusionary Practices: Nationalism, if not tempered with inclusivity, can lead to exclusionary practices. It may marginalize certain communities or groups that are perceived as not conforming to the dominant nationalist narrative, undermining the principles of equality and diversity.
- Authoritarianism: In some instances, nationalism can be manipulated to support authoritarian regimes. Leaders who exploit nationalist sentiments might curtail individual freedoms, suppress dissent, and weaken democratic institutions in the name of national security or unity.
- Historical Revisionism: Nationalism can sometimes lead to the revisionist interpretation of history, selectively highlighting certain events or figures to fit a particular narrative. This distortion of historical facts can contribute to misunderstanding and perpetuation of stereotypes.
- Xenophobia and Isolationism: Extreme nationalism can foster a sense of superiority or exceptionalism, leading to xenophobia and isolationism. This may hinder international cooperation and collaboration, limiting the exchange of ideas and hindering progress on a global scale.
- Cultural Homogenization: Excessive nationalism may lead to the imposition of a single cultural identity, suppressing regional or minority cultures. This homogenization can erode the rich tapestry of diversity that defines India’s cultural landscape.
- Diversion of Resources: Nationalistic fervor, if not balanced, may divert resources away from critical issues such as education, healthcare, and social welfare. Overemphasis on nationalistic agendas can hinder the holistic development of the nation.
- Aggressive Nationalism and Militarization: Nationalism, when channeled aggressively, may contribute to militarization and an arms race. Excessive focus on military strength as a symbol of national pride can divert resources away from essential social and economic development.
- Lack of International Cooperation: Extreme nationalism may lead to a reluctance to engage in international cooperation. This can limit India’s participation in global initiatives and partnerships, hindering progress on issues that require collective action. In conclusion, while nationalism has played a pivotal role in India’s history, it is crucial to approach it with a balanced perspective to avoid the potential disadvantages associated with extreme or exclusionary forms of nationalism. Striking a balance that embraces diversity, inclusivity, and a commitment to democratic values is essential for the sustainable and harmonious development of the nation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the dynamics of nationalism in India are nuanced, marked by a tapestry of advantages and disadvantages that have significantly shaped the nation’s trajectory. The advantages, such as the unification of a diverse populace, the successful struggle for independence, and the preservation of cultural identity, underscore the positive impact of nationalist fervor. These aspects have contributed to India’s resilience, global recognition, and ongoing development.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential disadvantages associated with nationalism. Issues like ethnic and religious tensions, regional disparities, and exclusionary practices highlight the challenges of navigating a path between unity and diversity. The risk of historical revisionism, authoritarianism, and cultural homogenization further underscores the need for a balanced and inclusive approach to nationalism.
As India continues to evolve, it is imperative to foster a nationalism that embraces diversity, safeguards individual freedoms, and promotes social justice. A responsible and inclusive form of nationalism can serve as a catalyst for progress, fostering a sense of collective purpose without compromising the principles of democracy and equality. Striking this delicate balance will be essential for India to navigate the complexities of the modern world while preserving the values and ideals that form the foundation of its national identity. Ultimately, the evolution of nationalism in India remains an ongoing journey, one that requires constant reflection, adaptability, and a commitment to the principles that define the nation’s character.
Certificate Of Completion
Certificate of Completion
[Student’s Name][Class/Grade Level]This is to certify that I, [Student’s Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the project on “History Project On Nationalism In India For Class 10th.” The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
In this project, I delved into in-depth research and analysis, investigating various facets and relevant theories related to the chosen topic. I demonstrated dedication, diligence, and a high level of sincerity throughout the project’s completion.
Key Achievements:
Thoroughly researched and analyzed History Project On Nationalism In India For Class 10th.
Examined the historical background and evolution of the subject matter.
Explored the contributions of notable figures in the field.
Investigated the key theories and principles associated with the topic.
Discussed practical applications and real-world implications.
Considered critical viewpoints and alternative theories, fostering a well-rounded understanding.
This project has significantly enhanced my knowledge and critical thinking skills in the chosen field of study. It reflects my commitment to academic excellence and the pursuit of knowledge.
Date: [Date of Completion]Signature: [Your Signature] [School/Institution Name][Teacher’s/Examiner’s Name and Signature]
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download History Project On Nationalism In India For Class 10th PDF






