
Food Supply Chain In India Class 12 Project
THE FOOD SUPPLY CHAIN OF INDIA
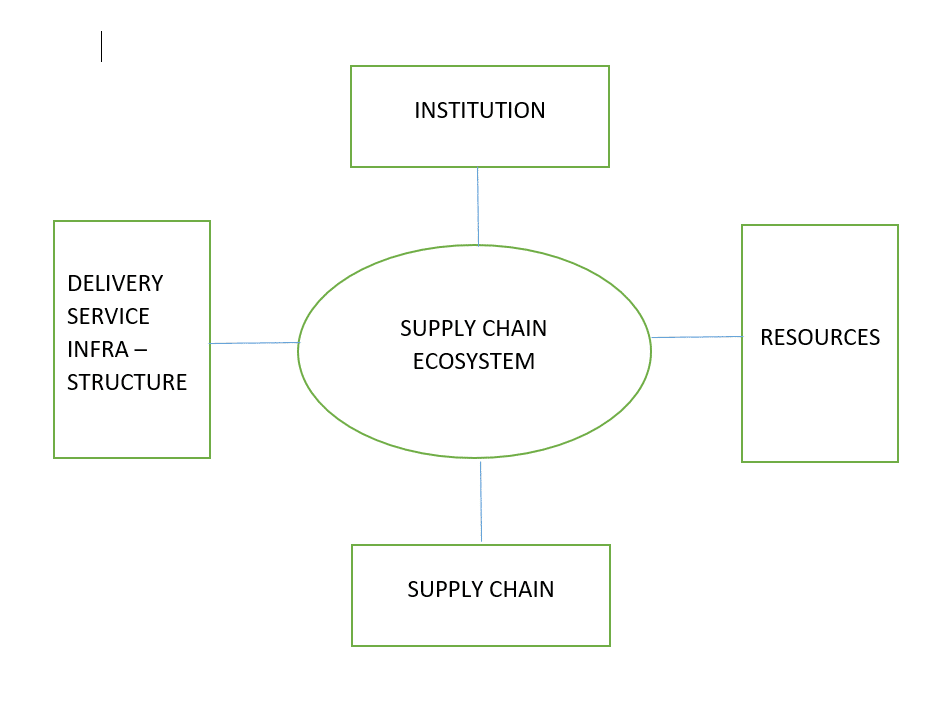
THE ECOSYSTEM REVIEW
THE BASIC ECOSYSTEM
Investment Climate- co- Evolution risk propagation
SES FRAMEWORK CAN HELP US TO STUDY
- GOVERNANCE
- Innovation
- Risk
- Performance
SUPPLY CHAIN REDESIGN
- HIGH PERFORMANCE SUPPLY CHAIN Efforts of stakeholders for last two decades are highly risk prone
- Tesnion between weak and strong ties among chain partners
- Globalisation has created long supply chain which are fragile and need monitoring
- Governance which involves partners selection coordination and executes takes centre stage.
FOOD SUPPLY CHAINS ARE COMPLEX SYSTEM
Food supply chains are highly complex interacting networks that link millions of small players such as farmers, Kirana shops, hawkers, industries, governments and other organisations affecting the political and economical climate.
We should Recognize
- The complexity of social political and operational issues.
- The doamin knowledge to be acquired.
- The analytics needed to build excellence in strategy and execution and metegate the risks.
- The appropriate governance structure needed to fulfill the promised deleveries.
AGRI SERVICE ECOSYSTEM IN INDIA

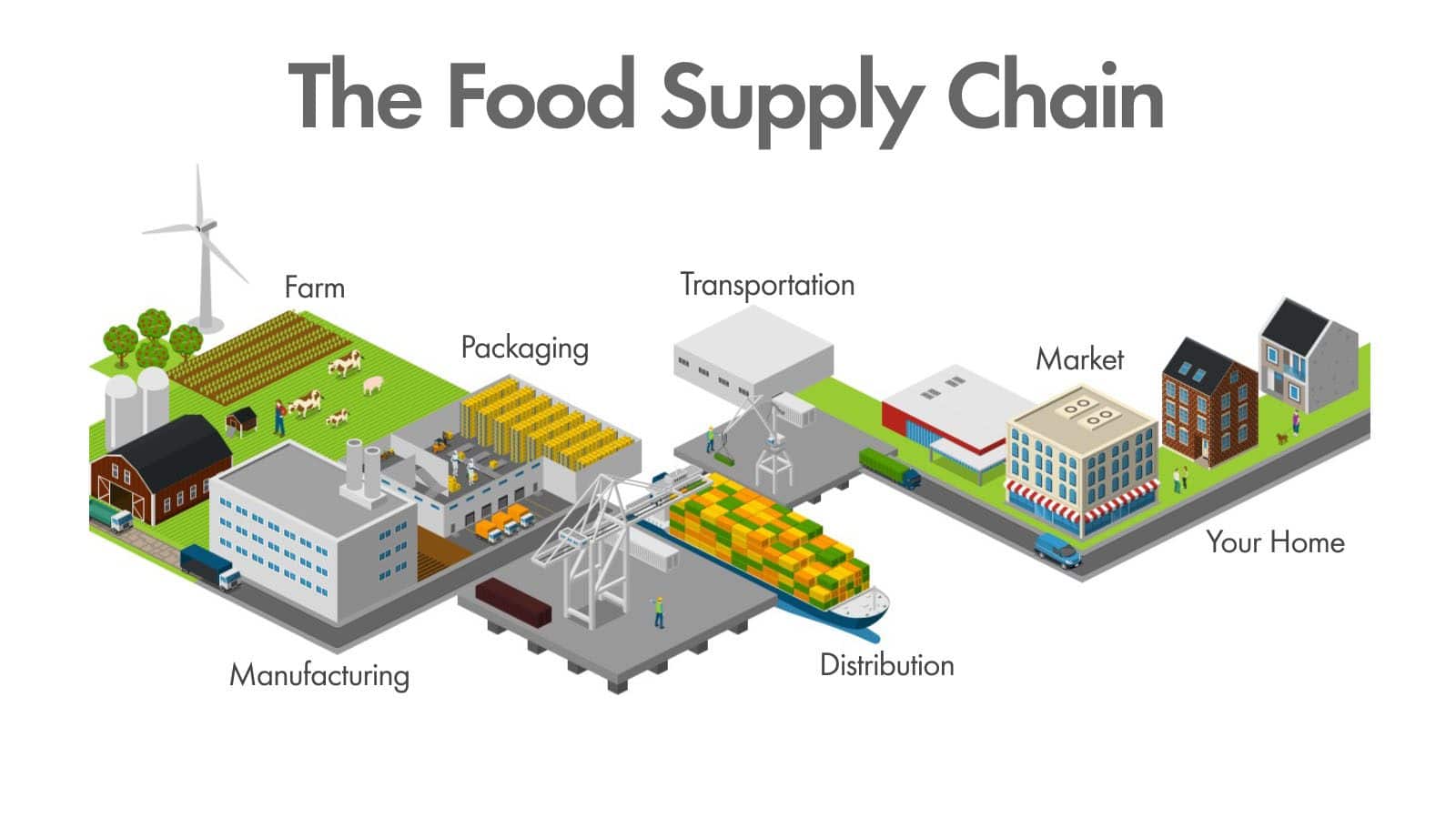
THE FOOD SUPPLY
A food supply chain consists of [processes and activities that take food from its raw material form (from fark to cark). Food supply chain management is developing as a research discipline, spanning local, regional natural and its international area and it has progressed from a series of shorter independent transactions to more collaborative relationships between producers, processors manufacturers and retailers. Food supply chains are confronted with increased consumer demands for food quality and sustainability. When redesigning their chains the analysis of food quality change and environmental load for new scenarios is as important as the analysis of efficiency and responsiveness requirements
THE PLOUGH PLATE FOOD SUPPLY CHAIN
- The supply chain involves formers, seed producers fertilizers, financial institutions, millers, Government, warehouses, fair price shops, retail shops, railways, trucks, transport companies etc.
- The plough plate supply chain does not use machines and distirbution takes placce from village to mandi.It is the distirbution centre for farmers.
SUPPLY CHAIN INEFFICIENCIES
- 106 Million Small farmers
- 400 Million agri workers
- 12 Million Kirana shops
- 1.5 Million Hwakers
- Too many intermediares
- Manual handling
- Improper packaging
- Standard for hygiene
- Not demand driver:No contract forming
- Subsidized pricing
- Public Distribution Ineffeciennces
- reach to customers is different
FOOD MANUFACTURING

- Only a small percentage of fresh produce or meat are processed.
- Port harvest research and food product are testing are at a very nascent stage.
- Negatives on food manufacturing in India
- Food Manufacturing is expensive
- High import duties on processing and packaging machinery
- High sales tax on packaged products
- high protein food not available
Processed food is more expensive than freshly cooked food.
INSTITUTION: REGULATORY & SOCIAL FACTORY
Agriculture produce Marketing Committee (APC) ACI

- The APMC ACT in each state of India require all agriculture products to be sold only in Government regulated markets called Mandis.
- This market impose substantial taxes on buyers in addiction to commission and fees taken by Government.
- Under the present Act. The processing industry cannot buy directly from farmers and the farmer is also restricted from entering into direct contact with any manufacturing
- Result: Disintegrated supply chain.
MANDI: FARMERS’ MARKET

- The APMC, which regulates Mandis, was amended in many states.
- Companies still cannot buy only can lease fertile land from the farmer.
- They can buy waste land or lease it
- Retailers find it difficult to work directly with the farmers and change the Mandi mechanism
- The Mandis remains more price-competitive.retailes source from mandis instead of developing their own supply chains
- Supply chain is as efficient as that
GOVERNMENT INTERVENTION POLICIES
- The minimum support price offered by the government for 24 crops acts as insurance for farmers against price fluctuation and provides inputs to the POS.
- The essential commodities act empower the govy to control productio,distribution and pricing etc to secure equitable distribution and fair pricing etc to secure equitable.this restricts interesting movement of goods
- These regualtions may have cost their utility and are hampering the growyh and moderation of organised retail.
SUPPLY AND DEMAND IN RETAIL SUPPLY CHAIN
Diagram
RESOURCES AND MANAGEMENT THE INDIAN ADVANTAGE
- In India 52% of land is cultivated and world average iss 71%
- All 15 major cimates of the world are in Indua9snow hot Himalayas to hot humid southern peninsula)
- India has 20 agro climate regions and 46 of 60 in soil types
- Sunshine hours and day length ideally suitable for year round crop cultivation.
- Mega centre for biodiversity in plants,animals,insects micro-organism and accounts for 17% animal,12% plants and 10% fish genetic resources of the globe.
- Live stock sector:india has 16% of cattle 57% of buffalos,17% goats of teh world.
INDIA AGRICULTURE

- Agriculture contributes 14.7% to GDP,43B exports and employs more than 50.0% of countries work force.
- india has more than 106M small farm holdings
- Seond highest fruit and vegetable producer iin the world and cold storage available only for 10%
- Seconf highest producer of milk additional cold storage needed
- Fifth largest producer of eggs cold chains are more
- Sixth largest producer of fish
SEED- FEEF: VALUE DRIVEN AGRICULTURE
- CURRENT SCENARIO,SUPPLY DRIVEN
The farmer is unwawre of the market,crops sometthing and tries ro sell in a mandi or to an agent and expects a fair price and immediate payment. - DESIRABLE SCENARIO
The farmer crops to market demands the right grade of produce and sells to right customer to get maximum income. - NEED TO TRANSFORM
The way agriculture works,create business orientations among the farming commiunity
STANDARDS
A standardisation is a powerful tool for improving supply chain efficiency. Standards enable partners to enable better compatibility and interoperability of their systems and processes.
There are two kinds of standards in the food supply chain
- The food standard that concerns the manufactruing processes,contest and packaging etc for daily,poultry,rady eat foods.
- The logistics and IT systems standardtisation concerns the crtoon,pallets and IT system software so that seamless transfer of good and information is possible.
DELIVERY SERVICE INFRASTRUCTURE
COLD CHAIN
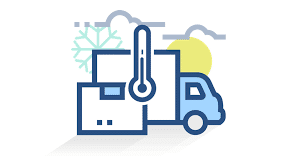
Cold Chain provides facilities for storage for perishables from origin to point of consumption in order to pressure quality and ensure longer life.
Cold chain infrastructure includes
- Pre-cooling facilities,cold storage,refrigerates carriers
- Multi-Model transportation
- Information management system,WMRS,RFID
These are in short supply in India
DISTRIBUTION LOGISTICS IN INDIA
- Fragmented,Individual company based,technology sophistication,not integrated into the supply chain.
- Current attempts are to build hard infrastructure and no attempt to soft infrastructure such as tradefacilation,ERP,WMS sensor Networks.
- Losses due to helf,spoilage,goods damage due to manual handling,long lead time and resultant supply chain ineffeciencies
- India ranks 46 on the 2012 Logistic Performance Index.
CHALLENGES FACING THE RETAIL SECTOR
Unavailability of logistics companies offering back end support for retailers
- Refrigerated transport and warehouse facilities.
- Timely distribution of supplies to retail outlets
- The lack of efficient and organised supply chain management leading to higher costs and complexity of sourcing and planning for retailers and hence to consumers
- Unavailability of sufficiently skilled and trained manpower leads to trial and error management in retail operations.
USE EXISTING FACILITIES MORE FRUITFULLY
Take advantage of the vast network and logical capabilities of the existing institutions such as post offices, road transport corporations, banks etc to bring a host of services to rural populations. Do not wait for the infrastructure to be available.
FOOD SAFETY AND HYGIENE
- Need to assure consumers about safety and quality of food.
- the sanitary and phytosanitary(SPs) agreement under wto has lead to increasing recognition and adoption of food safety measure
- Compliance with intternational food standards is a perquisite t o gaina higher share of world trade
- Concerns on food,safety on the back of breakout of diseases such as BSE,Avian influenza,Bird Flu,etc.
- Grwoing consumer demands for products whih are healthy.
STATE OF FOOD SUPPLY CHAIN IN INDIA
- Very Inefficient
- Needs good Governance
- Need food processing Industry
- Needs cold chains logistics
- Need Immediate actions
CONCLUSION
The supply chain involves farmers seeds, producers, fertilizers factories, financial institutions millers, government, warehouses, fair price shops, retail shops, railways, truck transport companies etc. It is a paradox that it has pros as well as cons too. Its positive side is the stored food in excess can be used during severe conditions like famine etc. Also, it could be given to poor strata of the society in low prices which they can afford called issue price which is usually less than the market.\
BIBLIOGRAPHY
INTERNET
www.cbseguide.com
www.foodssupply.com
MAGAZINE
Economic Agriculture
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Food Supply Chain In India Class 12 Project PDF






