
Biology Project On Diabetes For Class 11th & 12th
What is Diabetes
Diabetes, an enduring metabolic enigma, disrupts the body’s meticulous handling of glucose, the quintessential energy source. When carbohydrates make their grand entrance, they’re gracefully transformed into glucose, a fuel that courses through our bloodstream. To orchestrate this energy ballet, we rely on insulin, a hormone crafted by the pancreas.
However, in the realm of diabetes, insulin takes a different path. There are two main deviations:
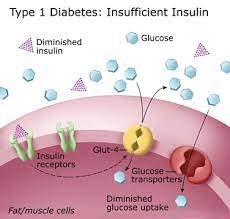
Insufficient Insulin Production (Type 1 Diabetes):
- Type 1 diabetes, often a childhood companion, can strike at any age.
- It’s an autoimmune saga where our body’s defense system turns rogue, targeting and annihilating the very creators of insulin – the beta cells in the pancreas.
- This onslaught results in a meager supply of insulin or sometimes none at all, leading to glucose’s struggle to enter cells, thereby elevating blood sugar levels.
Ineffective Insulin Utilization (Type 2 Diabetes):
- Type 2 diabetes, a more seasoned player, usually emerges in adulthood, although it’s gaining traction among younger generations.
- Here, insulin encounters a fickle reception by our cells, akin to a missed handshake. The cells resist its charms.
- Initially, the pancreas labors overtime to churn out more insulin, but with time, it may not meet the demand, causing blood sugar to ascend.
Type 1 Diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes, a childhood voyage into the unknown, occasionally intrudes later in life.
- An autoimmune plot unfolds, where the immune system, muddled in its judgment, lays siege to the pancreatic beta cells.
- To counter this betrayal, lifelong insulin therapy through injections or insulin pumps becomes a necessity.
- It’s a rarity, comprising a mere 5-10% of diabetes cases.
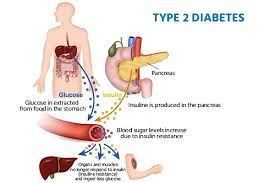
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Type 2 diabetes, a common tale, often waits until adulthood to make its entrance, but not always.
- The plot thickens with insulin resistance and an underwhelming insulin production.
- Lifestyle factors, like diet and exercise (or lack thereof), play pivotal roles in its script.
- Many times, it can be tamed with lifestyle changes, encompassing diet, exercise, and occasionally, oral medications or insulin therapy.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Unquenchable Thirst: Diabetes begets an unrelenting thirst (polydipsia), driven by excessive urination and fluid loss.
- Frequent Pit Stops: The sugar surge in the bloodstream leads to a constant restroom rendezvous (polyuria) as the body attempts to rid itself of the sugar surplus.
- Mysterious Weight Loss: Despite a ravenous appetite and hearty meals, weight loss becomes an unsolved mystery. Glucose’s elusive energy dance leaves its mark.
- Weariness: Elevated blood sugar levels cast a cloud of fatigue and general malaise.
- Vision’s Blur: The lens of the eye falls victim to the sugar surge, clouding vision with a hint of blur.
- Sluggish Healing: Diabetes plays the role of a slow conductor in the orchestra of wound healing, extending the recovery time.
Causes of Diabetes
The diabetic saga unfolds through various threads, depending on the type:
Type 1 Diabetes:
- It’s a genetic inheritance with a twist, sparked by an autoimmune rebellion. The body’s guardians turn on the pancreatic beta cells.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Here, lifestyle wields significant influence. Obesity, sedentary living, dietary choices, and genetics intertwine. Insulin resistance steals the limelight.
Who is at Risk For Diabetes
Factors that Heighten Risk:
- Family History: A family tree laced with diabetes makes one more susceptible to its embrace.
- Obesity: Carrying extra weight, especially around the waistline, serves as a red flag, particularly for Type 2 diabetes.
- Physical Inertia: A sedentary existence raises the curtain on insulin resistance, ushering in a higher risk of diabetes.
- Unwholesome Diets: Diets rich in sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed fare are prime suspects in the diabetes lineup.
- Age Matters: Diabetes often nods to age as a key player, especially after the 45-year mark.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic backgrounds, like African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, bear a heavier diabetes burden.
HIV and Diabetes
- Antiretroviral Medications: The tools we wield against HIV can, paradoxically, fan the flames of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance, elevating diabetes risk.
- Inflammation Intrigue: The chronic inflammation sparked by HIV infection can cast a shadow of insulin resistance.
- Risk Factor Overlap: HIV and diabetes share a sinister commonality – shared risk factors, including obesity and a lackadaisical lifestyle.
- Screening Mandate: The elevated risk of diabetes among those living with HIV mandates regular diabetes screenings.
Treating Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin therapy reigns supreme here. It’s a daily ritual of insulin injections or the grace of an insulin pump to orchestrate blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The treatment tableau encompasses lifestyle alterations (diet and exercise), oral medications to curb blood sugar, and, in some acts, insulin therapy.
- Prediabetes: This precursor is tamed through lifestyle transformations. It’s the art of weight loss, routine physical activity, and dietary tweaks to thwart the progression to Type 2 diabetes.
How is Diabetes Managed
- Blood Sugar Surveillance: Keeping tabs on glucose levels is akin to orchestrating a symphony – it’s pivotal for making medication and lifestyle adjustments.
- Medicinal Arsenal: Depending on the diabetes type and its intensity, metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin might take the stage.
- Lifestyle Tune-Up: The harmony of healthy eating, regular exercise, and weight management is the backbone of diabetes management.
- Check-Ups are Key: Regular visits to healthcare maestros for check-ups and screenings are non-negotiable in the diabetes score.
Prevention
- Nutrient-Packed Fare: A diet brimming with wholesome foods, fiber, and judicious sugar intake is the first line of defense.
- Physical Rhythm: Choreographing regular exercise routines maintains a healthy weight and bolsters insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Watch: Shedding extra pounds, especially that stubborn abdominal fat, is a powerful weapon against diabetes.
- Screening Vigilance: Those at risk should embrace routine diabetes screenings as a preventive measure.
Conclusion
Diabetes weaves a tapestry of complexity, entwining genetics, lifestyle, and environmental threads. While it can be managed through a blend of medications, lifestyle shifts, and vigilant monitoring, the true hero is prevention. Understanding the intricate dance of these factors is key to tackling the diabetes challenge head-on.
Bibliography:
- American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Diabetes Risk Factors.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). HIV and Diabetes.
- International Diabetes Federation. (n.d.). Diabetes Complications.
- World Health Organization. (2016). Global Report on Diabetes.
Certificate of Completion
[Student’s Name][Class/Grade Level]This is to certify that I, [Student’s Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the project on “Diabetes For Class 11th & 12th.” The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
In this project, I delved into in-depth research and analysis, investigating various facets and relevant theories related to the chosen topic. I demonstrated dedication, diligence, and a high level of sincerity throughout the project’s completion.
Key Achievements:
Thoroughly researched and analyzed Biology Project On Diabetes For Class 11th & 12th.
Examined the historical background and evolution of the subject matter.
Explored the contributions of notable figures in the field.
Investigated the key theories and principles associated with the topic.
Discussed practical applications and real-world implications.
Considered critical viewpoints and alternative theories, fostering a well-rounded understanding.
This project has significantly enhanced my knowledge and critical thinking skills in the chosen field of study. It reflects my commitment to academic excellence and the pursuit of knowledge.
Date: [Date of Completion]Signature: [Your Signature] [School/Institution Name][Teacher’s/Examiner’s Name and Signature]
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Biology Project On Diabetes For Class 11th & 12th PDF






