Design and Fabrication of the V8 Engine Project
Introduction
The V8 engine, an icon of power and efficiency in the automotive world, stands out for its unique configuration and impressive performance. Known for its eight-cylinder piston setup in a V configuration, the V8 engine has been the heart of many high-performance vehicles. This article explores the design and fabrication process of the V8 engine, highlighting its components, operation, and the meticulous engineering behind this mechanical marvel.
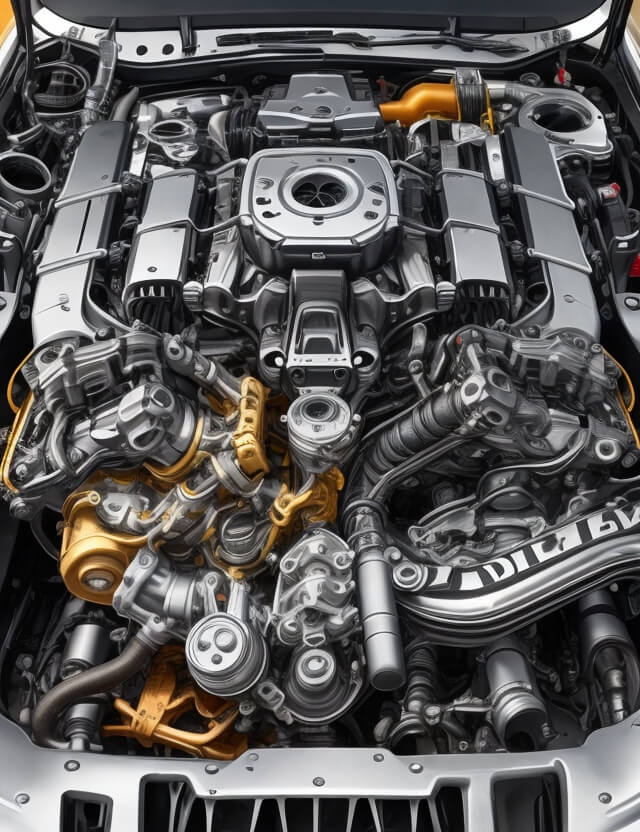

Understanding the V8 Engine
- Configuration: The V8 engine consists of two banks of four cylinders arranged at a typical V-angle of 90 degrees, sharing a common crankshaft. This setup offers a compact design while maintaining balance and reducing vibrations.
- Cross-Plane Crankshaft: Most V8 engines utilize a cross-plane crankshaft, which contributes to the engine’s smooth operation and characteristic sound.
- Displacement and Power: Modern V8 engines vary in displacement, typically ranging from 3.5 to 6.4 liters, with some variations outside this range for specific performance or luxury applications.
Design and Fabrication Process
- Frame and Materials: The engine’s frame is often made from durable materials like mild steel or aluminum, with MDF used for prototyping or educational models. Components like pistons, rods, and camshafts are precision-crafted from metal alloys.
- Crankshaft and Pistons: The crankshaft is the backbone of the engine, converting linear piston motion into rotational motion. Pistons are connected via rods to the crankshaft, moving synchronously to generate power.
- Valve Mechanism: A belt and pulley arrangement drives the cams, which in turn control the timing and movement of the inlet and outlet valves, ensuring efficient air and fuel flow into and out of the combustion chambers.
Components
- Crankshaft: Converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Cylinders and Pistons: Where fuel combustion takes place, driving the pistons.
- Piston Rods: Connects the pistons to the crankshaft.
- Belt & Pulley Arrangement: Transfers motion from the crankshaft to the camshafts.
- Cams and Springs: Control the opening and closing of engine valves.
- DC Motor (for demonstration models): Simulates the engine’s operation in educational or display models.
- Frame: Provides structural support, often made from metal or wood.
Advantages of the V8 Engine
- High Performance: Known for producing significant power and torque, making it a favorite in performance and luxury vehicles.
- Smooth Operation: The V8’s natural balance leads to smooth operation with less vibration, contributing to a comfortable driving experience.
- Iconic Sound: The distinct rumble of a V8 engine is unmistakable and often associated with power and prestige.
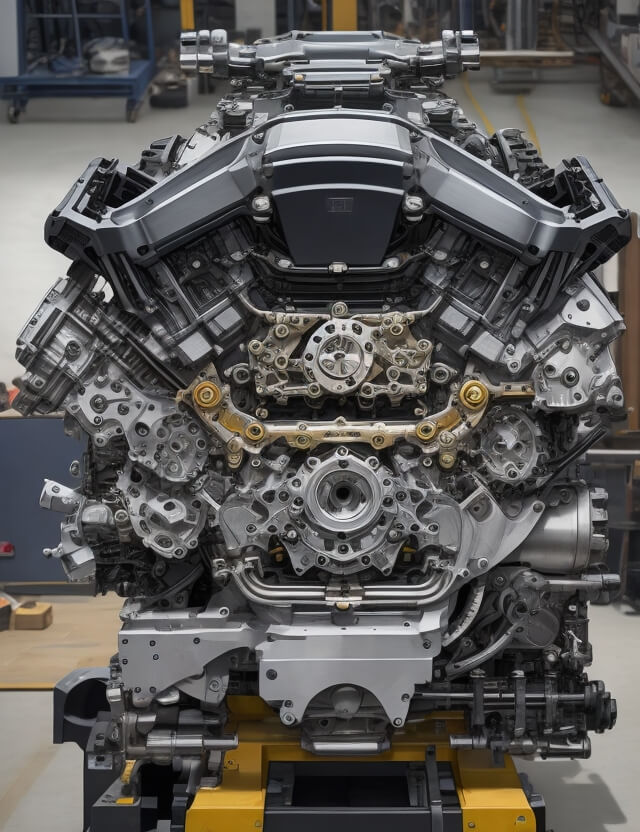

Conclusion
The V8 engine remains a symbol of automotive excellence and engineering prowess. Its design and fabrication involve a deep understanding of mechanics, dynamics, and materials science. Whether powering a luxury sedan or a high-performance sports car, the V8 engine continues to captivate enthusiasts and engineers alike with its power, performance, and charisma.
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Design and Fabrication of the V8 Engine Project PDF






