
Psychology Project Class 12 CBSE – Schizophrenia
HISTORY:
The word schizophrenia – which translates roughly as “splitting of the mind” and comes from the Greek roots Schein [ to split] and phren [mind] was coined by Eugene Bleuler in 1908 and was intended to describe the separation of functions between personality, thinking, memory and perception. American and British interpretation of Bleuler leads to the claims that he described its main symptoms as A’s:
Flattened affects, autism, ambivalence, and impaired association of ideas.
Bleuler realized that the illness was not a demotion, as some of the patients improved rather than deteriorated and thus proposed the term schizophrenia instead.
Treatment was revolutionized in the mid-1950s with the development and introduction of chlorpromazine.
In the early 1970s, the diagnostics criteria for schizophrenia were the subject of a number of controversies while eventually led to the operational criteria used today. It became clear after the 1971 US_UK diagnostic study that schizophrenia was diagnosed to a far greater extent in America than in Europe. These were some of the whole DSM manuals, recently in the publications of the DSM-III in 1930.
The term schizophrenia is commonly misunderstood to mean that affected persons have a “split personality.” Although some people diagnosed with schizophrenia may hear voice and may experience the choice as distinct personalities, schizophrenia does not involve a person changing among a distinct, multiple personalities, schizophrenia does not involve the confusion arises due to literal interpretation of Bleuler’s term “schizophrenia [Bleuler originally associates schizophrenia with dissociation and included split personality in his category of schizophrenia]. Dissociative identify disorder [having a split personality] was also often misdiagnosed as schizophrenia based on the loose criteria in the DSM-II. The first known misuse of the term to mean “split personality” was in an artist by the poet T.S Eliot in 1933. Other scholars have traced earlier roots. Rather the term means a “splitting of mental function reflecting the presence of the illness.”
- Disorder – Schizophrenia
- Specialty – Psychiatry
- Symptoms – False reliefs, Confused thinking, Voices
- Usual Unset – Early adulthood
- Duration – Chronic
- Causes – Environment and genetic factors
- Risk Factor – A problem during pregnancy, raised in a city
- Diagnosis Method – Counseling, job training
- Treatment Medication – Antipsychotics
- Prognosis – 18 years shorter life expectancy
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
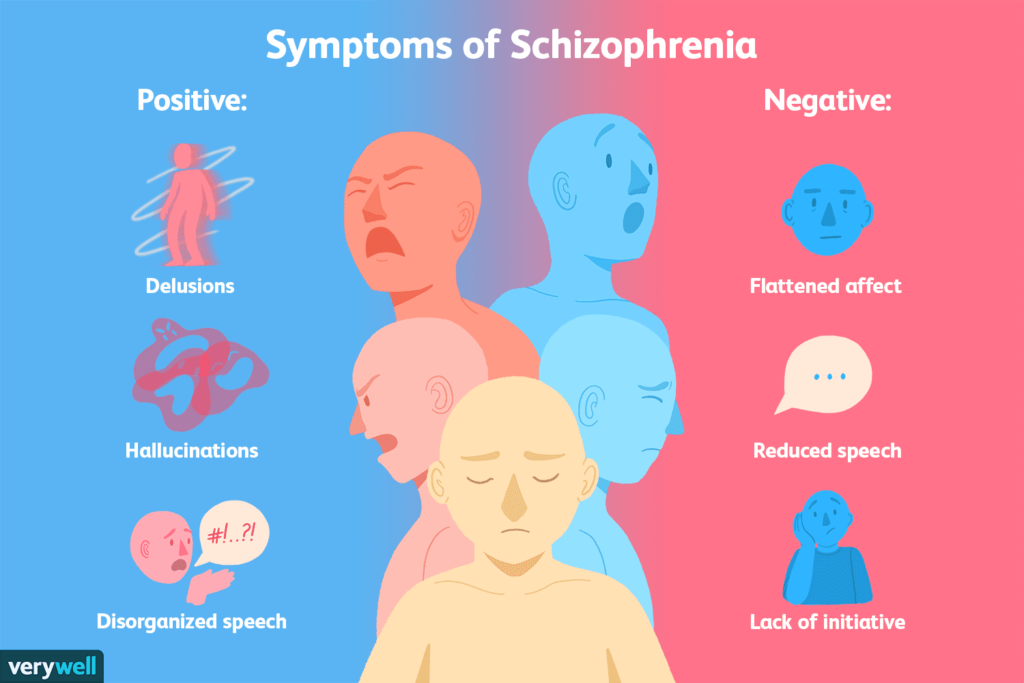
Individuals with schizophrenia may experience hallucination [ most reported are hearing voices] delusion and disorganized thinking and speech. That may range from loss of train of thought to sentence only connected in meaning, to speech that is not understandable known as word salad social withdrawals, sloppiness and hygiene, and loss of motivation and judgment are all common in schizophrenia.
Distortions of self-experience such as feeling as if one’s thoughts or feeling s are not really one’s own to reliving thoughts are being inserted into one’s mind sometimes termed passively phenomenon is also common. There is often an emotional difficulty, for example, lack emotionally responsive, particularly to stressful or negative stimuli and that such withdrawal, irritability, dysphoria and clumsiness before the onset of the diseases children who go on to develop schizophrenia may also demonstrate decreased intelligence, decreased motor development, isolated play preferences, social anxiety, and poor school performances.
CAUSES
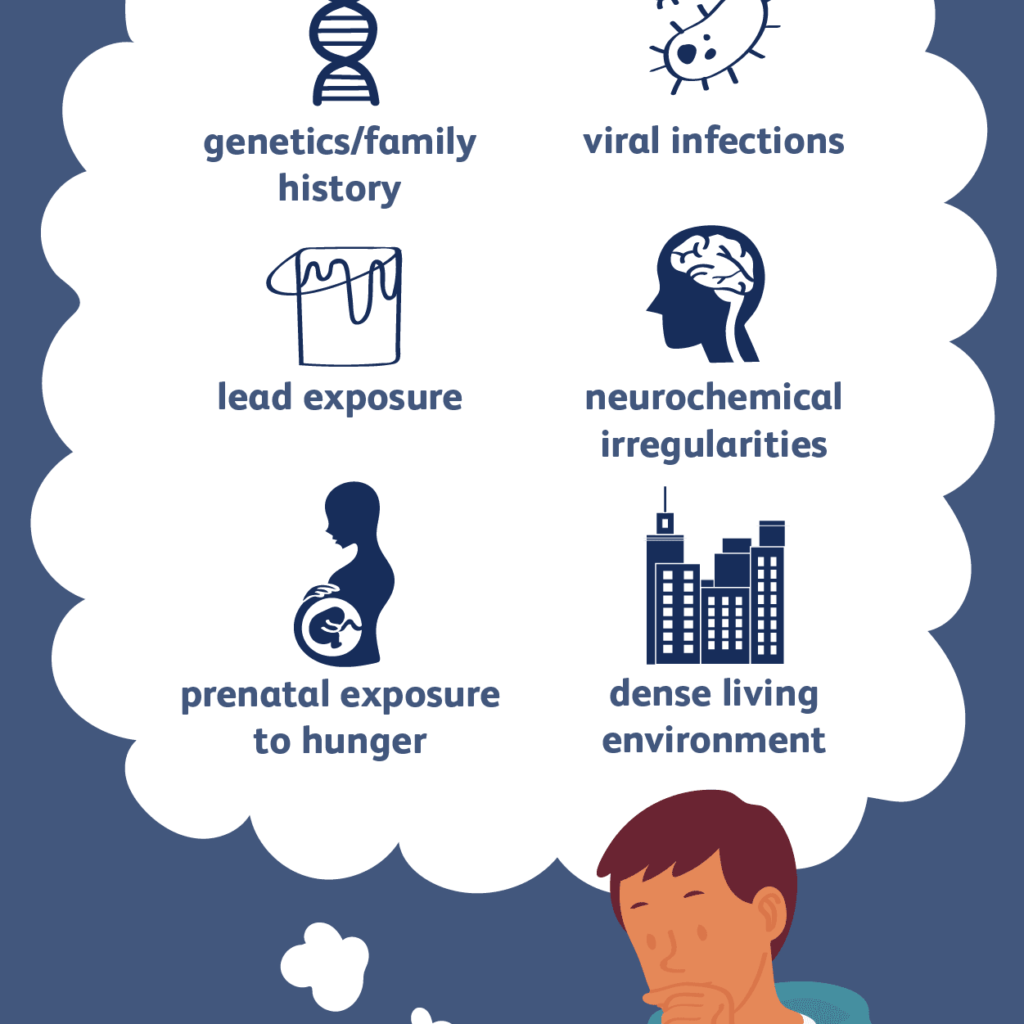
A combination of genetic and environmental factors play a race in the development of schizophrenia. People’s inter-family history of schizophrenia who have a technique has a 20-40% chance of being diagnosed one year later.
GENETIC FACTORS
An estimate of heritability varies because of the difficulty in separating genetic and environmental influences, averages of 0.80 have been given. The greatest single risk factor for developing schizophrenia has a first-degree relative with the disease more than 40%, negative stimuli, and such sensitivity may cause vulnerability to symptoms or be the disorder. Some evidence suggests that the context of delusional beliefs and psychotic experience can reflect emotional causes of the disorder and that now a person interprets such experience can influence symptomatology. Further evidence for the role of psychological mechanisms comes from the effects of psychotherapies on symptoms of schizophrenia.
POSITIVE SYMPTOMS
Positive symptoms are those that most individuals do not normally experience, but are present with schizophrenia. They can include delusion, disordered thought, and speech and tactile, auditory, visual, olfactory, and gustatory typically regard as Manifestation of psychosis. Hallucinations are also typically related to the content of the delusional theme.
NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS
These are deficits of normal emotional responses or to other thought processes and less responsive to medications. They commonly include flat expressions or little emotions, poverty, lack of form relationships, lack of motivation. Negative symptoms appear to contribute more to people’s quality of life, functional, and the other than symptoms do. People with greater negative symptoms often have a history of poor adjustment before the onset of illness, and response to medications is often limited.
COGNITIVE DYSFUNCTION
The deficit in cognitive activities is widely recognized as a core feature of schizophrenia. The extent of the cognitive deficit an individual’s experiences are the predictions of how functional an individual will be in maintaining treatment. The presence and degree of cognitive dysfunction in an individual with schizophrenia has been reported to be an indicator of functionality than the presentation of positive or negative symptoms. The deficits impacting the cognitive function are found in a large number of areas: working memory, long-term memory, semiotic processing, episodic memory, attention, learning.
ONSET
Late adolescence and early adulthood are peak periods for the onset of schizophrenia, critical years in a young adult social, and sanction development. In 20% of men and 23% of women diagnosed with schizophrenia, the condition manifested itself before the age of 19-20 minimize the developmental disruption associated with schizophrenia, much work has recently been done to identify and treat the pre-onset phase of the illness, which has been detected up to 30 months before the onset of symptoms. Those who go on to develop schizophrenia may experience transient or self-thinking psychotic symptoms of social.
SUBSTANCE USE
- Almost half of those with schizophrenia use drugs or alcohol excessively. Puephetonime, cocaine, and to lesser extent alcohol, can result in a transmit stimulant psychosis or alcohol-related psychosis that present very similarly to schizophrenia although it is not generally believed to cause of the illness, people with schizophrenia use nicotine at a much higher rate than the general population
- Alcohol use can occasionally cause the development of the chlorine, induced psychotic disorder via a kindling mechanism. Alcohol use is not associated with an earlier onset of psychosis.
- Cannabis can be a contributory factor in schizophrenia, potentially causing the disease in those who are already at risk.
MEDICATION
The first time psychiatrist treatment for this is antipsychotic medication, which can reduce the positive symptoms of psychosis in about 7 to 14 days. Antipsychotics, however, fail to improve negative symptoms and cognitive dysfunction significantly. Those on antipsychotics, continued use decrease the risk of release. However, the use of antipsychotics can use to dopamine hypersensitivity, increasing the wish of symptoms if antipsychotics are stopped.
The choice of which to use is based on benefits, risks, and costs. It is debatable whether, as a class, typical or typical antipsychotics are amisulpride, olanzapine, risperidone, and clozapine may be more effective are associated with greater side effects. Typically antipsychotics have equal drop-out, and symptoms replace races to when used at low to moderate dosages.
There is a good response in 40-50%, a postal response in 30-40% acid treatment resistance failure of symptoms to responds satisfactorily after in weeks schizophrenia occurs along with obsessive-compulsive disorder[OCD] considerably more often than could be explained by chance, although it can be difficult to distinguish obsession that occurs in OCD from the delusion of schizophrenia.
PREVENTION
Prevention of it is difficult as there are no reliable for the later development of the disorder. There is tentative evidence for the effectiveness of early inventions to prevent schizophrenia. While there is some evidence that early intervention of those with a psychotic episode may improve short-term outcomes, there is a little benefit from these measures after five years. Accounting to prevent schizophrenia in the prodrome phase is to uncertain benefit and, therefore, as of 2009, is not recommended. Cognitive-behavioral therapy may reduce the risk of psychosis in those at high risk.
TYPES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
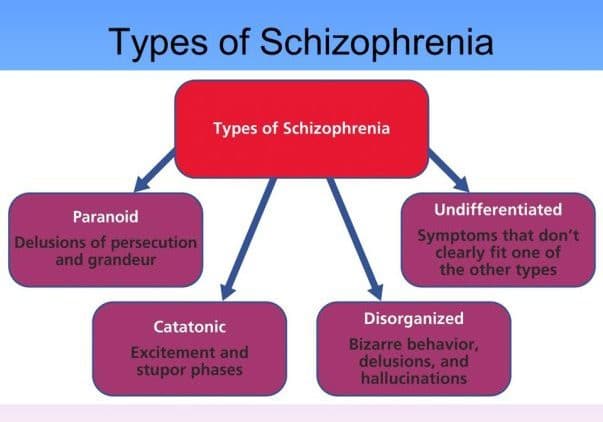
- Paranoid: delusions or authority hallucinations are present, thought disorder, disorganized behavior, or affecting flattering are an illusion and persecutory and organized, put some addition to these, either themes such as religiosity or somatic may be present.
- I have disorganized: named hebephrenic schizophrenia in the ICD where thought disorder and flat affects are present together.
- Catatonic: the subject may be almost immobile or exhibit agitated purposes. Symptoms can include and waxy flexibility.
- Undifferentiated: psychotic symptoms are present, but the criteria for paranoid, disorganized, or catatonic types have not been met.
- Residual: where the positive symptoms are present at a low intensity only.
DIFFERENTIATED DIAGNOSIS
Psychotic symptoms may be present in several other mental disorders, including borderline personality disorder, drug intoxication, and drug-induced psychosis. Delusion is also present in delusional disorder, and social withdrawal in social anxiety disorder and social avoidant personality disorder has symptoms that are similar out less severe than those of schizophrenia, and being unloved or abused increases the risk of psychosis. Living in an urban environment during childhood or as an adult has consistently even found to increase the risk of schizophrenia by a factor even after taking into account drug user, and size and social group, other factors that play an important role include social isolation schizophrenia and imagination related to social adversity. Racial discrimination, family dysfunction, unemployment, and poor housing conditions.
It has been hypothesized that in some people, the development of schizophrenia is related to dysfunction such as the sun with non-celiac gluten sensitivity or abnormalities in the intestinal flora. A subgroup of a person with schizophrenia presents an immune response to gluten different from that found in people with celiac, with elevated of certain serum.
MECHANISMS
A number of attempts have been made to explain the link between altered brain function and schizophrenia. One of the most common is the domains hypothesis, which attributes psychosis to the mind’s faulty interpretation of the misfiring of aspanimgic neurons.
PSYCHOLOGICAL
Many psychological mechanisms have been implicated in the development and maintenance of schizophrenia. Cognitive basis has been identified in those with the diagnosis or those at risk, epically when under stress or in a confusing situation. Some cognitive features may reflect global neurocognitive deficits such as money loss, while others may be related to particular issues and experiences.
DEVELOPMENT FACTORS
Factors such as hypoxia and infection, or stress and malnutrition schizophrenia in the mother during fetal development, may result in a slight increase in the risk of schizophrenia are more likely to have been in winter or spring/ at least in the northern hemisphere, which may be a result of increased of viral exposure in the uterus. The increased risk is almost five to eight percent. Other inflection during pregnancy is around one time with that may increase the risk included toxoplasma Gondi and Finlandia.
RESEARCH DIRECTIONS
Research has found a tentative benefit in using to treat schizophrenia. Nidotherapy is changing the environment to improve their ability to function is also being studied; however, there is not enough evidence to make a conclusion about its effectiveness.
Negative symptoms have proven a challenge to treat, as they are generally not made better by medication of various agents have been exposed for possible benefits in this area, there have been trials on drugs with anti-inflammatory activities used on the premises that inflammation a role in the pathway might play schizophrenia.
Management
The primary treatment of schizophrenias antipsychotic medications, often in combination with psychological and social supports. Hospitalization may occur for either voluntarily or [if mental legislation allows it ] involuntarily. Long-term hospitalization is uncommon since dunstisthonatization beginning in the 1950s, although it still occurs. Community support service, including drop-in centers, visits by members of a community mental health team, supported employment and supports group, is common. Some evidence indicates that regular exercise has a positive effect on the physical and mental health of those with schizophrenia.
PROGNOSIS
Schizophrenia has great human and economic costs. It represents a decreased life expectancy by 10-20 years. This is primarily because of its association with obesity, poor diet, sedentary lifestyles, and smoking, with an increased rate of suicide playing a lesser role, antipsychotic medications may also increase the risk. These differences in life expectancy increased between the 1970s and 1990s.
Schizophrenia I a cause of disability with active psychosis ranked as the third most disability after guardipragia and dementia and of paraplegia and blindness.
Approximately three-fourths of people with schizophrenia have ongoing disability with relapse, and [6.7 million people globally are deemed to have moderate or severe disability from the condition. Some people do recover completely, and others function well in society. Most people with schizophrenia independently with community supports. About 85% are unemployed. People with the first episode of psychosis a good long-term outcome occurs in 42%, an immediate outcome 35%, and a poor outcome in 27%. Outcomes for schizophrenia appear better in the developed world.
SOCIETY AND CULTURE VIOLENCE

People with the same mental illness, including schizophrenia, are at a significantly greater risk of being victims of both violent and non-violent crimes. Schizophrenia has been associated with a higher rate of violent acts but not appear to be related to associate substance abuse. Rate of homicides liked to psychosis are similar to those linked to substance misuse, and parallel the overall rate in a violence independent of drug misuse is controversial, but certain aspect if individual historic or mental states may be factor absent 11% of people in prison suicide have been schizophrenia had while 2% have mood disorder. Ameer’s study found about 8-10% of people in which schizophrenia has had committed a violent act in the past year compared to 2% of the general population.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT:
I am very thankful to everyone who supported me, for I have completed my project effectively and moreover on time. I am overwhelmed in all humbleness and gratefulness to acknowledge my depth to all those who have helped me to put these ideas well. I am equally thankful to my psychology teacher Mrs.Ritu. She gave me moral support and guided me in difficult matters regarding the topic with the help of valuable suggestions and encouragement. I would like to thank my parents, who, despite their busy schedule, gave me different ideas in making this project unique.
CERTIFICATE
Certified that this is the bonafide work of KUDRAT of class XII-A of Lawerence public senior secondary school.
He/she has performed this project during the academic year 2018-19.
A number of projects certified _____ out of _____ in psychology.
Teacher’s signature
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Psychology Project Class 12 CBSE – Schizophrenia PDF






