
Economics Project on Globalisation – CBSE Class 12
INTRODUCTION:
The term globalization is derived from the word globalize, which refers to the emergence of an international network of the economic systems. Since its inception, the concept of globalization has inspired competing for definition and interpretations, with antecedents dating back to the great movements of trade and empire across Asia and the Indian ocean from the 15th century onwards. Due to the complexity of the concept, research projects, articles, and discussions often remain focused on a single aspect of globalization. Globalization can be located on a continuum with the local, national, and regional. At one end of the continuum lie social and economic relations and networks which are organized on a local on a national basis at the other end lie social and economic relations which crystallize the wider scale of global interactions.
OBJECTIVE
- To know more about the Globalisation and also about its Merits and Demerits.
- To understand about the behand the globalization.
- To analysis the value measures of globalization.
- To know about the positives and negatives of the globalization in the Economy.
NEEDS AND SIGNIFICANCE:
- It helps to know about the interconnection between two or more countries.
- It helps to know more about the transfer of goods and services.
- Globalization makes the whole market into one as it reduces the barriers across the world.
- Globalization helps to access technology as it helps in more production propose in the international market.
HISTORY:
There are both distal and proximate causes, which can be traced to the historical factors affecting globalization. Large-scale globalization began in the 19th century. Globalization is not a new phenomenon. For centuries individuals have been buying and selling goods to individuals in other lands. Through the years, globalization has continued to spread through the passing of information and communication. International commodity markets, labor markets, and capital markets make up the economy and define economic globalization. Beginning as early as 4000 BCE, people were trading livestock, tools, and other items. In early civilization, in Mesopotamia, a token system was the first form of commodity money.
GLOBALISATION:
Globalization refers to the integration of markets in the global economy, leading to the increased interconnectedness of national economies, or it is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. Markets, where globalization is particularly common, to include financial markets, such as capital market, money and credit market and insurance market, commodity markets, including markets for oil, coffee, tin and gold, and product market, etc. MNC’s that are Multi-National Countries are playing a major role in the process of globalization. More and more goods and services, investments, and technology are moving between countries. This is the integration of economies, industries, markets, culture, and policymaking around the world. Globalization describes a process by which national and regional economies, societies, and cultures have been integrated through the global network of trade, communication, immigration, and transportation. In the more recent past, globalization was often primarily focused on the economic side of the world, such as trade, foreign direct investment, and international capital flow, more recently the team has been expanded to include a broader range of areas and activities such as culture, media, technology, socio-cultural, political and even biological factors, e.g., climate change. Globalization is defined as a system related to increasing interaction, growing economic independence, and widening economic integration is the world economy. It encourages the integration of the economy of the country with the world economy. It is an outcome of a set of various policies that are aimed at transforming the world towards greater interdependence and integration. It involves the creation of networks and activities transcending economic, social, and geographical boundaries. It encourages foreign trade, private and institutional foreign investment. It practically removes all hindrance and restriction of foreign trade.
CHARACTERISTICS OF GLOBALISATION:
Globalization is a process of deeper integration between countries and regions of the world involving:
- Greater trade across the border in goods and services.
- An increase in transfers of capital, including the expansion of foreign direct investment (FDI) by transnational companies (TNCs) and the rising influence of Sovereign Wealth Funds. Fifty-one of the largest economies in the world are corporations.
- The development of global brands that serve markets in lower, middle, and higher-income countries.
- Greater use of outsourcing and offshoring of production. The classic example is the iPhone, which is part of a complex global supply chain. The product was conceived and designed in Silicon Valley in the USA, and the software enhanced by engineers working in India. Most iPhones are assembled in China and Taiwan.
- High levels of labor migration both within and between countries.
- New nations joining the trading system, for example, Russia joined the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2012. The latest countries to join the WTO are Yemen (2014), Seychelles (2015), Kazakhstan (2015), and Afghanistan (2016).
- A shift in the balance of economic and financial powers from developed to emerging economies and markets – i.e., a change in the center of gravity in the world economy.
- Increasing spending on capital investment, innovation, and infrastructure across a large part of the world.
- Globalization is a process of making the world economy more connected and inter-dependent.
- Many industrializing (emerging) countries are winning a rising share of world trade, and their economies are growing faster than developed nations. Emerging and developing countries now account for more than 57% of global GDP adjusted for purchasing power according to 2015 data published by the IMF. The 28 – nation European Union has a share of global GDP that is the Gross Domestic Products of less than 17%.
- Globalization reform allows free interaction of an economy with the rest of the world
Shares of World Economic Output in 2015
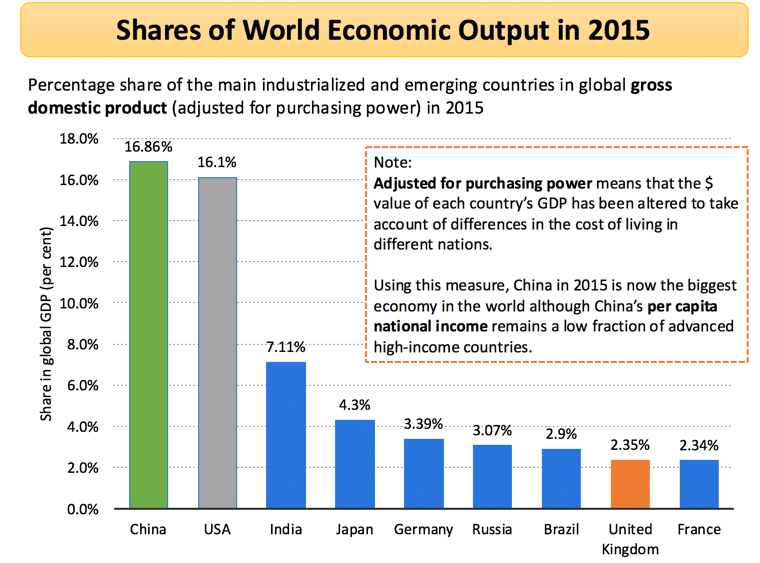
The percentage share of the main industrialized and emerging countries in the global gross domestic product (adjusted for purchasing power) in 2015
Note:
Adjusted for purchasing power means that the $ value of each country’s GDP has been altered to take account of differences in the cost of living in different nations
Using this measure, China in 2015 is now the biggest economy in the world, although China’s per capita national income remains a low fraction of advanced high-income countries.
Our new economic policy contributed to globalization in the following ways:
- Raising foreign equity participation.
- Devaluation of Rupee.
- Convertibility of Rupee.
- Long Period trade policy.
- Encouragement to open competition.
- Modification of custom and Tariffs.
ADVANTAGES OF GLOBALISATION:

- Globalization brings several potential benefits to international producers and national economies, including:
- Providing an incentive for countries to specialize and benefit from the application of the principle of comparative advantage.
- Globalization enables World Wide access to sources of cheap raw materials, and this enables from to have cost comparative in their market and overseas markets.
- In the long term, increased trade is likely to lead to the creation of more employment in all countries that are involved.
- Globalization has been able to establish links is such a way that the happening (advancement) in India can be influenced by events happening miles away from the rest of the world.
- Globalization has been able to turn the world into one whole on creating a boundary-less world as it provides easy asses to the global market.
- We are now exposed to advance technology and can develop indigence production in the international markets.
- Globalization should be seen as an opportunity in the teams of greater asses to global markets and increase the possibility of large industries of developing countries to become an important player in the international arena.
DISADVANTAGES OF GLOBALISATION:

There are also several disadvantages of globalization as the coin had two sides with it:
- Jobs may be lost because of the structural changes arising from globalization. Structural changes may lead to structural unemployment and may also widen the gap between rich and poor within a country.
- Increased trade associated with globalization has increased pollution and helped contributed to Co2 emission and global warming. Trade growth has also accelerated the depletion of non-renewable resources such as oil.
- Globalization has compromised the welfare and identity of people belonging to poor counties.
NEGATIVE EFFECT
- Developed nations have outsourced
- Exploitation of labor
- Job insecurity
- Sophisticated weapons enhancing their ability
- Bad aspects of foreign cultures
- Taken over
- Reduced the government’s ability
IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION IN INDIAN ECONOMY:

- The impact of globalization has been highly positive in almost all spheres of economic and social life and virtually no negative effects.
- India’s economic growth has been high, exports have boomed, incidence of poverty has been reduced, employment has surged, begging by India for economic and has stopped, long term inflation rate has gone down, scarcely of goods have disappeared, the quality of products available have improved substantially and overall India has become progressively vibrant and internationally competitive.
- The service sector is the lifeline for the social, economic growth of a country.
- The real reason for the growth of the service sector is due to the increase in urbanization, privatization, and more demand for intermediate and final consumer services.
- In advanced economies, the growth in the primary and secondary sectors is directly dependent on the growth of services like banking, insurance, trade, commerce, entertainment, etc.
Economic Impacts:
- Greater Numbers of Jobs:
The advent of foreign companies and growth in the economy has led to job creation. However, these jobs are concentrated more on the services sector, and this has led to the rapid growth of the service sector creating problems for individuals with low levels of education. The last decade came to be known for its jobless growth as job creation was not satisfied with the level of economic growth.
- More choice to consumers:
Globalization has led to a boom in the consumer product market. We have a range of choices in selecting goods, unlike the times where there were just a couple of manufacturers.
- Higher Disposable Incomes!
People in cities working in high paying jobs have a higher income to spend on lifestyle goods. There has been an increase in the demand for products like meals, eggs, pulses, organic food as a result. It has also led to protein inflation.
IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION ON INDUSTRIAL SECTOR:

- The effect of globalization on Indian industry started when the government opened the country’s markets to foreign investment in the early 1990s.
- The globalisation of the Indian industry took place in its various sectors, such as steel, cement, retail, pharmaceutical, petroleum, chemical, textile, and BPO, which helps in providing employment.
- Globalisation has increased across the world in recent years due to the fast progress that has been made in the field of technology, especially in transport and communication. The government of India made changes in its economic policy in 1991 by which it allowed direct foreign investment in the country.
- Globalisation helps in reducing the level of unemployment and the poverty level in the country.
- The benefit of the effect of globalisation on the Indian industry is that the foreign companies brought in highly advanced technology with them, and this helped to make the Indian Industry more technologically advanced.
- The negative effects of globalisation on the Indian industry are that with the coming of technology, the numbers of labor required decreased, and this resulted in many people being removed from their jobs. This happened mainly in the pharmaceutical, chemical manufacturing, and cement industries.
OUTSOURCING:
This is one of the most important outcomes of the globalisation process. In outsourcing, a company hires a regular service from external sources, mostly from other countries, which was previously provided internally or from within the country like [legal advice, computer service, advertisement, securities each provided by the respective department of the country) a form of economic activity. Outsourcing has been intensified in the recent times because of fast modes of communication, particularly the growth of information technology with the help of modern telecommunication links including internet, the text, voice, and visual data in respect of these are digitized and transmitted in real-time over the continents and national companies. Most Multi-National Corporations and even small companies are outsourcing their services to India, where they can be availed at a cheaper cost with a reasonable degree of shell and accuracy.
LPG MODEL IN INDIA:
After Independence in 1947, the Indian government faced a major problem in developing the economy and to solve issues. Considering the issues pertaining at that time, the government decided to follow LPG Model [Liberalization, Privatization, and Globalisation model]. The economic growth conditions of India at that time were not very good. This was because it did not have proper resources for the development, not in terms of natural resources but terms of financial and industrial development. At that time, India needed the path of economics, and for that use, the Five Years Plan concept of which was taken from Russia and feet that it will provide a fast development like that of Russia, under the view of the socialistic pattern society. India had practiced several restrictions ever since the introduction of the first industrial policy resolution in 1948.
FINDINGS:
- More and more Multi-National Companies (MNCs) are looking for locations around the world that are cheap for their production because MNCs are playing a major role in the globalisation process.
- Globalisation has benefited well- off consumers and also producers with skill, education, and wealth. Many small producers and workers have suffered as a result of rising competition.
- Fair globalization would create opportunities for all and also ensure that the benefits of globalization are shared better.
CONCLUSION:
Globalisation is the process of rapid integration of countries. This is happening through greater foreign trade and foreign investment. Technology, particularly IT, has played a big role in organizing production across countries. Also, the liberalization of trade and investment has facilitated globalisation by removing barriers to trade and investment. Globalisation is now a reality, and the question is how to make globalisation fairer? Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all, and also ensures that the benefits of globalisation are shared better.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- www.ecoglob.com
- Science technology and globalisation.
- www.globalWorld.com.
- NCERT textbook of class 11th, economics,
- NCERT textbook of class 12th business studies.
- NCERT textbook of class 8th economics,
DOWNLOAD PDF OF THE PROJECT

Password: hscprojects.com
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Economics Project on Globalisation – CBSE Class 12 PDF







It’s best for making project file. Thanks alotttttttttt!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Thanku…………..
Amazing project…..
Loved it
It helps me a lot in doing my project .
Thanks to your team
It helped a lot !!!!…