
Stock Exchange Project Class 12
INTRODUCTION TO STOCKS
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is a facility where stock brokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock and bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide for facilities the issue and redemption of such securities and instruments and capital events including the payment of income and dividends. The best way to let students learn is a stock exchange project class 12.
To be able to trade a security or a certain stock exchange, the securities must be listed there. Trade on a stock exchange is restricted to Brokers who exchange. In recent years, various other trading venues, such as electronic communication networks.
HISTORY OF STOCK EXCHANGE
The first stock exchange was officially formed in London in 1773, a scant 19 years before the New York Stock exchange. Whereas the Law Restricting shares handcuffed the London Stock Exchange (LSE), the NYSE has dealt in the trading of stocks, for better or worse, since its inception. The NYSE wasn’t the first stock exchange in the U.S. however, that honour goes to the Philadelphia Stock Exchange, but it quickly became the most powerful. Formed by Brokers under the spreading boughs of a buttonwood tree, NYSE made its home on wall street. It was in the heart of all the business and trade coming to and going from the United States, as well as the domestic base for most banks and large corporations.
INDIAN STOCK EXCHANGE
Indian Stock Exchanges may refer to the 18 official stock exchanges located in India, the largest of which are NSE and BSE. All of them are as follows: –
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) → Mumbai
- National Stock Exchange (NSE) → Mumbai
- Calcutta Stock Exchange (CSE) → Kolkata
- Cochin Stock Exchange → Kochi
- Interconnected Stock Exchange of India
- Multicommodity Stock Exchange
- OTC Exchange of India
- Pune Stock Exchange → Pune
- National commodity and derivatives Exchange
- P Stock Exchange
- Vadodara Stock Exchange
- Coimbatore Stock Exchange
- Madras Stock Exchange
- Meerut Stock Exchange
- Ahmedabad Stock Exchange
- Delhi Stock Exchange
- P Stock Exchange
- Hyderabad Stock Exchange
- Bangalore Stock Exchange
NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE

The National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE) is the leading stock exchange in India, located in Mumbai. It is established in 1992 as the first demutualized electronic exchange in India, and so it was the first exchange to provide a modern, fully-automated system. Vikram Limaye is M.D and CEO NSE.
NSE has a total market capitalization of more than US $2.7 trillion, making it the world’s 11th largest stock exchange as of April 2018. NSE’s flagship index, NIFTY 50, the 50 stock index, is used extensively by investors in India and around the world as a barometer of Indian Capital Markets. Nifty Fifty Index was launched in 1996 by the NSE.
The stock trading at the BSE and NSE accounts for only around 4% of the Indian Economy, which derives most of its income-related activity from the so-called underdeveloped sector and households.
BOMBAY STOCK EXCHANGE
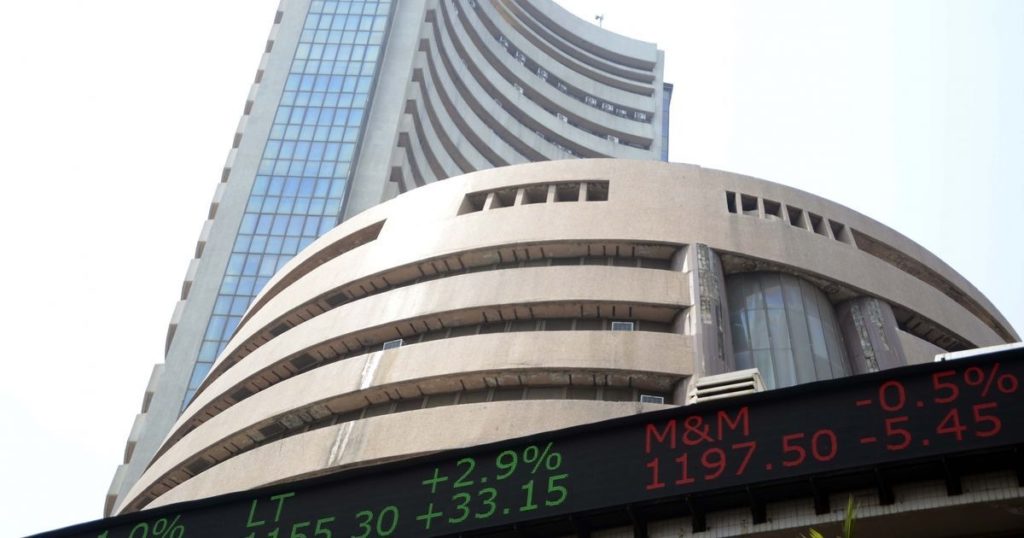

The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is an Indian Stock Exchange located at Dalal street Mumbai. Established in 1875, the BSE is Asia’s first stock exchange. It claims to be the world’s fastest stock exchange, with a median trade speed of 6 micro-seconds. It is also the world’s 10th largest stock exchange, with an overall market capitalization of more than $2.3 trillion as of April 2018.
Premchand Roychand founded the Bombay Stock Exchange. He was one of the most influential businesses in the 19th century. A man who made a fortune in the stockbroking business and came to be known as the Cotton King, the Bullion King, or just the Big Bull.
STOCK MARKET TIMINGS IN INDIA
Normal Trading Session:
- This is the actual time when most of the trading takes place.
- Its duration is between 9:15 AM to 3:30 pm.
- You can buy and sell stocks in this session.
- It follows a bilateral trading session, i.e., Whenever buying price is equal to the selling price; then the transaction is complete
Pre-Opening Session:
The duration is between 9:00 AM to 9:15 Am. This is further sub-divided into three sub-sessions:
- 9:00 AM to 9:08 AM: – This is the order entry session. You can place an order to buy and sell stocks during this duration.
- 9:08 AM to 9:12 AM: – This session is used to order matching and calculating the order price of the normal session.
- 9:12 AM to 9:15 AM: – This session is used as a buffer speed. It is used for the smooth translation of the pre-project session to the normal session.
- The time between 3:30 pm to 3:40 pm is used for closing price Calculation
- The closing price of a stock is the weighted average of the prices between 3:00 PM to 3:30 PM.
- For the indexes like Sensex & nifty, it’s the closing price is a time-weighted average of the constituent stocks for the last 30 mins, i.e., between 3 pm to 3:30 pm.
Post Closing Session
- The duration of the post-closing session is between 3:40 pm to 4:00 PM
- You can buy or sell stocks in the post-closing session at the closing price.
ROLE OF STOCK EXCHANGE
Stock exchange, apart from being the hub of the primary and secondary market, has a very important role to play in the economy of the country.
some of them are listed below:
- Raising capital for businesses
Exchanges help companies to capitalize by selling shares to the investing public.
- Mobilizing savings for investment
They help the public to mobilize their savings to invest in high yielding economic sectors.
- Facilitating company growth
They help companies to expand and grow by acquisition or fusion.
- Profit-Sharing
They help both casual and professional stock investors, to get a share in the wealth of profitability businesses.
- Cooperate governance
Stock exchanges improve stringent rules to get listed in them.
- Creating investment opportunities for small investors
Small investors can also participate in the growth of large companies.
- The government in Capital raises for development projects
They help govt to rise for development activities through the issue of bonds.
- Barometer of the Economy
They maintain the stock indexes, which are indicators of the general trend.
STOCK MARKET TERMINOLOGY

- Ask The price that a seller is willing to ask for a share of Stock.
- Back Testing: Applying the strategy to historical data to see if it is valid.
- Bear Market: A period of declining stock value, usually accompanied by investor pessimism.
- Block Trade: Buying or selling a large project, confidentially, it.
- Blue Chip: A established co. with a national or international reputation for stability, profitability, and value
- Blue Market: A period of rising stock value, usually accompanied by investor optimism in it.
- Bid: Price that a buyer is willing to pay for a share of stock.
- Close: The price of the stock at the end of the trading day.
- Dividend: A payment made of companies’ profits to their shareholders.
- Earnings per share (EPS): The Companies’ profit divided by the average number of outstanding shares.
- Electronic Communication Network (ECN): a Computer system that facilitates stock trading outside of a stock exchange.
- Fill or kill (Fok): – when you want all of your orders filled immediately or none at all.
- Fundamental Analysis: – Examining the financial health and strength of a company to determine its Share price, future value, and earning expectations.
- Hedge: – Limiting your classes or reducing risk by placing orders to cover two or more possible events in the market.
- Initial Public offering: When the first-time company issues its shares in public on an exchange.
- Limit Order: When you want to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better.
- Liquidity: Being able to sell or buy shares in a stock w/o the transaction seriously affecting the stock’s price.
- Margin: Borrowing money to trade for more than what you have in your account.
- Volume: The amount of a share being traded at a given point in time.
SEBI

In the 1980s, huge malpractices and frauds were emerging in the stock market of India. This was due to the huge sudden cash flow in the market.
Everyone wanted to get rich very quickly by finding loopholes in the system. The most prominent of those frauds was price rigging. The Union government of India noticed a decrease in figures and decided to form an organization, which can help recover the decrease in the financial market in India. SEBI was established in 1988. The primary role at that time was to observe the market, but SEBI had no power to control anything. It was a non-statutory body. To give it powers, the union govt of India passes the SEBI act 1992.
ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE OF SEBI
- There are main nine members on the SEBI Board
- One Chairman appointed by Govt. of India.
- Two members are officers from the union finance ministry.
- One number from RBI.
- Five members are appointed by the Union Govt of India, where three are whole-time members.
OBJECTIVES of SEBI
- To provide a transparent and healthy platform for corporates to raise funds from the financial market.
- To create and enforce bye-laws for corporations and financial intermediaries.
- To protect the right of investors and ensure the safety of their investment.
- Listen and provide a support system for investor grievances.
- Promote and Develop the financial market of India.
ROLE OF SEBI
SEBI was established to regulate the financial market of India. To achieve this objective, it takes care of the three most important entities of the financial Market, i.e.
- Issuers Of Securities
These are corporate entities that raise funds from the financial market. SEBI ensures that they get a transparent and healthy environment for their needs.
- Investors
These are the ones who keep the financial market alive. They earn from those markets; thus, it is the responsibility of SEBI to ensure that investors don’t prey on any manipulation or fraud in the market.
- Financial Intermediaries
These intermediaries act as a mediator in the financial market. Their presence brings smoothness and safety to financial institutions.
FUNCTIONS OF SEBI

- Protective Functions
As protective functions, SEBI performs the following functions:
- SEBI checks price rigging
- SEBI prohibits insider trading
- SEBI prohibit fraudulent activities and unfair trade practices
- SEBI sometimes educate the investors so that it becomes able to evaluate the Securities and always invest in profitable securities.
- SEBI issues guidelines to protect the interest of debenture holders
- SEBI is empowered to investigate cases of insider trading and has provisions for stiff fines and imprisonment
- SEBI has stopped the practice of allotment of preferential shares unrelated to market issues.
- Development Functions
- SEBI promotes the trading of intermediaries of the Securities Market
- SEBI tries to promote activities of the stock exchange by adopting a flexible and adaptable approach in the following way:
- SEBI has permitted internet trading through registered Stockbrokers.
- SEBI has made underwriting optional to reduce the cost of the issue. An even initial public offer of the primary market is permitted through the stock exchange.
- Regulatory Functions
- SEBI has framed sucks and regulations and a code to regulate the intermediaries.
- These intermediaries have been brought under the regulatory purview, and private placement has been made more restrictive.
- SEBI registers and regulates the working of Stockbrokers, sub, brokers, share transfer agents, trusties, merchant bankers, and all those who are associated with the stock exchange in many manners.
- SEBI registers and regulates the working of mutual funds, etc.
- SEBI regulates the takeover of the company (ies).
- SEBI conducts audits and inquiries of the stock exchange.
Top 25 LISTED COMPANIES
| Company Name | Last Price | % Chg | 52 wk High | 52 wk Low | Market Cap (Rs. Cr) |
| Reliance | 1278.05 | 0.66 | 1260.00 | 765.00 | 809.983.34 |
| TCS | 2042.20 | 0.33 | 2046.05 | 1210.33 | 781.671.62 |
| HDFC Bank | 2070.55 | -0.52 | 2219.05 | 1665.00 | 562.141.00 |
| HUL | 1781.75 | 0.56 | 1807.75 | 1169.00 | 305.483.63 |
| ITC | 310.35 | -0.32 | 317.00 | 250.35 | 379.366.25 |
| HDFC | 1918.70 | 0.65 | 2051.00 | 1638.00 | 324.320.96 |
| INFOSYS | 1379.95 | -1.38 | 1436.65 | 874.00 | 301.407.50 |
| MARUTI SUZUKI | 9161.40 | -0.65 | 10.000.00 | 7490.90 | 276.500.04 |
| SBI | 300.30 | -0.65 | 351.50 | 232.00 | 268.005.36 |
| KOTAK MAHINDRA | 1254.80 | 0.53 | 1424.00 | 962.30 | 230.257.74 |
| ONGC | 174.90 | 1.83 | 212.90 | 152.45 | 224.453.20 |
| ICICI BANK | 330.10 | -2.02 | 365.65 | 256.00 | 212.304.02 |
| LARSEN | 1342.80 | -0.72 | 1469.50 | 1116.45 | 168.250.02 |
| COAL INDIA | 290.40 | 0.62 | 316.56 | 236.70 | 180.283.16 |
| BAJAJ FINANCE | 2912.70 | 0.69 | 2944.15 | 1514.40 | 163.144.05 |
| AXIS BANK | 639.50 | 1.23 | 643.50 | 447.60 | 164.260.79 |
| SUN PHARMA | 629.65 | 0.46 | 645.00 | 434.92 | 151.073.40 |
| IOC | 154.25 | -0.20 | 231.30 | 150.15 | 149.004.57 |
| BHARTI AIRTEL | 368.50 | -0.12 | 548.50 | 331.20 | 147.304.15 |
| HCL TECH | 1023.45 | -0.15 | 1106.00 | 825.10 | 142.517.60 |
| NTPC | 154.25 | -0.10 | 187.95 | 149.45 | 136.431.75 |
| ASIAN PAINTS | 1392.50 | 0.97 | 1484.50 | 1862.00 | 133.563.25 |
| WIPRO | 292.30 | 2.62 | 334.75 | 253.50 | 132.231.80 |
| LEAD ZINC | 293.50 | 0.73 | 339.56 | 261.75 | 423.585.84 |
| M&M | 800.80 | 0.74 | 961.25 | 812.50 | 108.249.22 |
TRADING PROCEDURE
Step 1: Selection Of A Broker
The first step is to select a Broker who will buy or sell securities on behalf of the investors. This is necessary because trading of securities can only be done through SEBI’s registered brokers, who are members of the stock exchange.
Step-2: Opening Demat A/c With Depository
The next step is to open a Demat account. A Demat account refers to an account in which an Indian citizen must open with the depository participant to trade in listed securities in electronic form.
Step-3: Placing The Order
The next step is to place the order with the broker. The order can be communicated to the broker either personally or electronically.
Step-4: Executing The Order
According to the instructions of the investor, the broker buys or sells securities. The broker then issues a contract note. A copy of the contract note contains the name and the price of securities, brokerage charges, etc.
Step-5: Settlement
This is the last stage in the trading of securities done by the brokers on behalf of their clients.
The mode of settlement depends upon the contract. Equity spot market a T + 2 rolling settlement. Each exchange has its clearinghouse, which assumes all settlement risk.
| Name of Company | SBI | ITC | RELIANCE | KOTAK MAHINDRA | AXIS BANK |
| Share Price | 300,30 | 310.35 | 1278.05 | 1254.80 | 629.65 |
| Number of Shares Purchased | 32 | 32 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| Total Amount Invested | 9609.6 | 9931.2 | 10224.4 | 10038.4 | 10074.4 |
PORTFOLIO
An investment portfolio is a collection of assets owned by an individual or by an institution. An investor’s portfolio includes real estate and so-called ‘hard’ assets, such as a gold ban.
Imaginary Portfolio
Imaginary portfolio totalling a sum of approximately Rs. 50,000 in an of the five companies listed above.
TOTAL SHARES – 96
TOTAL AMOUNT INVESTED OUT
OF Rs. 50.000; 49878
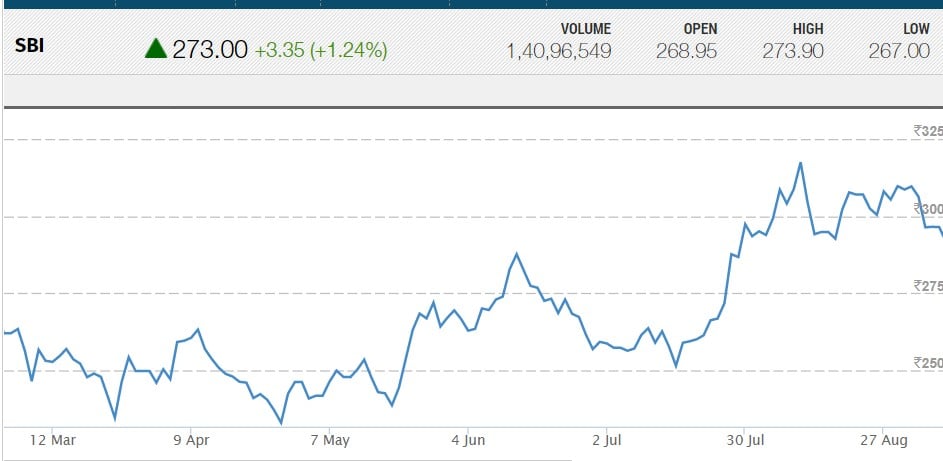
SBI
State Bank of India (SBI) is an Indian, multi-national, public sector banking and financial services company.
It is government-owned cooperation headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The company is ranked 217th on the Fortune Global 500 list of the world’s biggest corporations as of 2017. It is the largest bank in India with a 23% market share in assets, besides a share of ¼th of the total loan and deposits market.
The Bank descends from the Bank of Calcutta, founded in 1806, via the Imperial Bank of India, making it the oldest commercial bank in the Indian subcontinent, and it turns into SBI in the year 1955.
ITC
ITC Limited or ITC is an Indian based company, originally based in Kolkata, West Bengal. Its diversified business includes five segments: Fast Moving Manufactured Goods (FMCG), Hotels, Paperboards & Packaging, Agribusiness, and Information Technology.
Though the cigarette business contributes to more than 80% profits of the company, 80% of the capital is invested in the non-tobacco business.
Established in 1910, as the Imperial Tobacco Company of India Limited, the company was renamed Indian Tobacco Company Limited in 1970, and later to I.T.C and limited in 1974. The dots in the name were removed in 2001 for the company to be renamed ITC limited.
It employs over 30000 people at more than 60 locations across India and is part of the Forbes 2000 list.

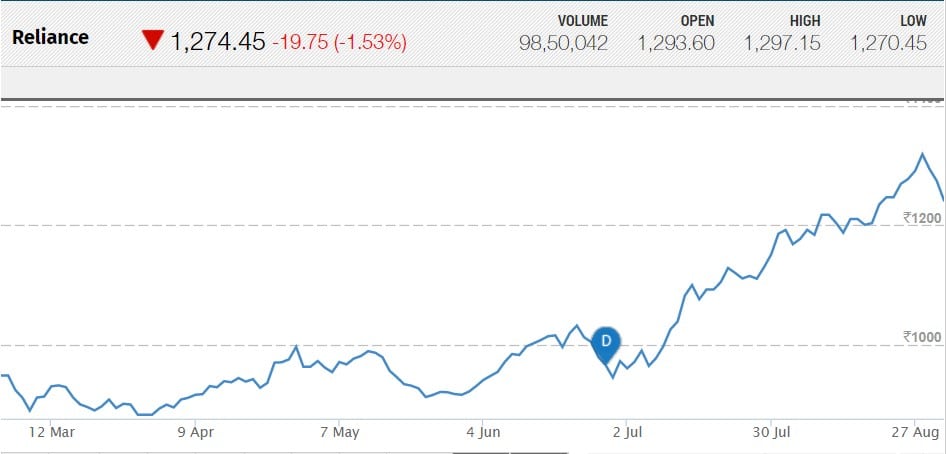
RELIANCE
Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) is an Indian conglomerate holding company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
Reliance owns businesses across India engaged in energy, petrochemicals, textiles, natural resources, retail, and telecommunications. It is one of the most profitable companies in India, the second-largest publicly traded co. in India by market capitalization, and it is the first company to reach $100 billion in market capitalization. The company is ranked 203rd on the Fortune Global 500 list of the world’s biggest corporations as of 2017. It continues to be India’s largest exporter, accounting for 8% of India’s total merchandise exports with a value of ₹147, 155 crores, and access to markets in 108 countries. It is also the highest income taxpayer in the private sector.
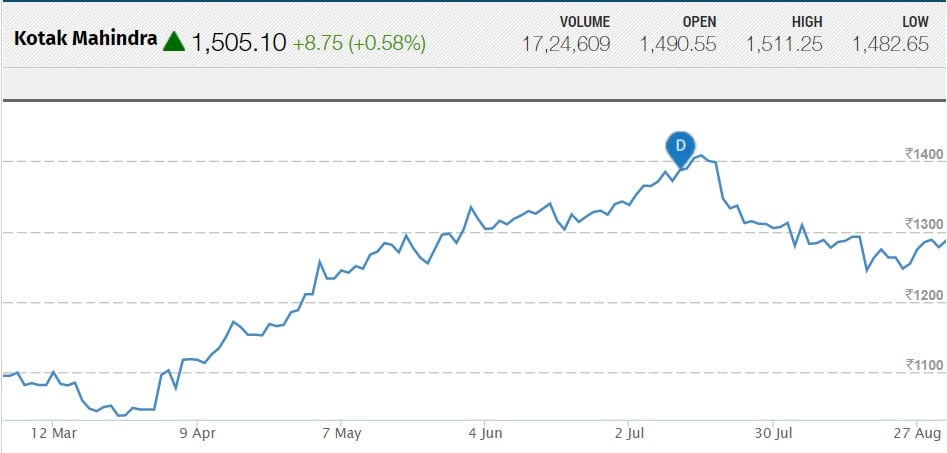
KOTAK MAHINDRA BANK
Kotak Mahindra Bank is an Indian Private Sector Bank headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. In February 2003, RBI gave the license to Kotak Mahindra Finance Ltd., the group flagship company, to carry on the banking business.
It offers a wide range of banking products and financial services for corporate and retail customers through a variety of delivery channels and specialized subsidiaries in the areas of personal finance, investment banking, general insurance, life insurance, and wealth management. Bank has a network of 1369 branches across 639 locations and 2163 ATMs in the country.
AXIS BANK
Axis Bank is the third-largest private sector bank in India, offering a comprehensive suite of financial products. Headquartered in Mumbai, it has a registered office in Ahmedabad. It has 3703 branches, 13814 ATMs, and nine international branches.
The Bank employed over 55000 people and had a market capitalization of ₹1.31 trillion. It sells financial services to large and mid-sized corporations, and SMEs.
As of 30 June 2016, 30.81% of shares are owned by promoters and their group. The remaining 69.19% are owned by Mutual Funds and others.
CONCLUSION
stock exchange conclusion
- Summarized Finding
- Over some time, many stock exchanges have been developed in India.
- The imaginary portfolio consists of SBI, ITC, Reliance, Kotak, and Axis Bank.
- The Negotiable Instrument Act governs stock exchanges.
- Quotations of share price include opening price, high price, low & closing price.
- Future Scope of Study
- To analyze movt. Of share prices.
- To analyze movt. Of the sharing process of various companies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I want to express my special thanks of gratitude to my teacher as well as our principal, who gave me the golden opportunity to do this wonderful stock exchange project class 12, helped me in doing a lot of research, and I came to know about so many new things. I am thankful to them. Secondly, I would also like to thank my parents and friends who helped me a lot in finalizing this project within the limited time frame.
CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that the class XYZ school, and he has completed his project under my supervision. He has taken proper care and shown almost sincerity in the completion of this stock exchange project class 12. I certify that this project is up to my expectations and as per the guidelines issued by CBSE
TEACHER’S SIGNATURE
EXAMINER’S SIGNATURE
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- BOOKS: NCERT, SUBHASH DEY
- TEACHERS
- FAMILY
- INTERNET
- https://www.moneycowbot.com
- https://en. wikipidia.com
- https://business.dictionary.com
- https://sebi.gov.in
DOWNLOAD PDF OF THE PROJECT

Password: hscprojects.com
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Follow On YoutubeSubscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Stock Exchange Project Class 12 PDF







This project was very helpful for me in completing my project.
Yes, this is very helpful for me and all students for doing this project I like
Superb it was 😊 thanks I completed my whole project by taking help from your site thanks alot for such a wonderful project.
Very Very helpful for my project…thanks for sharing this
Its really helpful.
Thank you
How to get the pdf of this project
Follow on zomato as mentioned and share your email